Deep Learning Image Processing Enables 40% Faster Spinal MR Scans Which Match or Exceed Quality of Standard of Care : A Prospective Multicenter Multireader Study
- PMID: 34846555
- PMCID: PMC8894206
- DOI: 10.1007/s00062-021-01121-2
Deep Learning Image Processing Enables 40% Faster Spinal MR Scans Which Match or Exceed Quality of Standard of Care : A Prospective Multicenter Multireader Study
Abstract
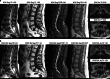
Objective: This prospective multicenter multireader study evaluated the performance of 40% scan-time reduced spinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstructed with deep learning (DL).
Methods: A total of 61 patients underwent standard of care (SOC) and accelerated (FAST) spine MRI. DL was used to enhance the accelerated set (FAST-DL). Three neuroradiologists were presented with paired side-by-side datasets (666 series). Datasets were blinded and randomized in sequence and left-right display order. Image features were preference rated. Structural similarity index (SSIM) and per pixel L1 was assessed for the image sets pre and post DL-enhancement as a quantitative assessment of image integrity impact.
Results: FAST-DL was qualitatively better than SOC for perceived signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and artifacts and equivalent for other features. Quantitative SSIM was high, supporting the absence of image corruption by DL processing.
Conclusion: DL enables 40% spine MRI scan time reduction while maintaining diagnostic integrity and image quality with perceived benefits in SNR and artifact reduction, suggesting potential for clinical practice utility.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Imaging; MRI; Spine.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S. Bash: Subtle Medical honoraria and consultant. B. Johnson: Subtle Medical honoraria. W. Gibbs: Subtle Medical honoraria. T. Zhang: Previous employee of Subtle Medical. A. Shankaranarayanan: Employee of Subtle Medical. L.N. Tanenbaum: Subtle Medical honoraria and consultant. Institution (RadNet): compensation for scanner use.
Figures

References
-
- Xu J, Gong E, Pauly J, et al. 200x low-dose PET reconstruction using deep learning. 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

