Establishing a risk assessment framework for point-of-care ultrasound
- PMID: 34846557
- PMCID: PMC8964607
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-021-04324-4
Establishing a risk assessment framework for point-of-care ultrasound
Abstract
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) refers to the use of portable ultrasound (US) applications at the bedside, performed directly by the treating physician, for either diagnostic or procedure guidance purposes. It is being rapidly adopted by traditionally non-imaging medical specialties across the globe. Recent international evidence-based guidelines on POCUS for critically ill neonates and children were issued by the POCUS Working Group of the European Society of Pediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC). Currently there are no standardized national or international guidelines for its implementation into clinical practice or even the training curriculum to monitor quality assurance. Further, there are no definitions or methods of POCUS competency measurement across its varied clinical applications.
Conclusion: The Hippocratic Oath suggests medical providers do no harm to their patients. In our continued quest to uphold this value, providers seeking solutions to clinical problems must often weigh the benefit of an intervention with the risk of harm to the patient. Technologies to guide diagnosis and medical management present unique considerations when assessing possible risk to the patient. Frequently risk extends beyond the patient and impacts providers and the institutions in which they practice. POCUS is an emerging technology increasingly incorporated in the care of children across varied clinical specialties. Concerns have been raised by clinical colleagues and regulatory agencies regarding appropriate POCUS use and oversight. We present a framework for assessing the risk of POCUS use in pediatrics and suggest methods of mitigating risk to optimize safety and outcomes for patients, providers, and institutions.
What is known: • The use POCUS by traditionally non-imaging pediatric specialty physicians for both diagnostic and procedural guidance is rapidly increasing. • Although there are international guidelines for its indications, currently there is no standardized guidance on its implementation in clinical practice.
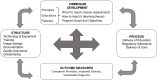
What is new: • Although standards for pediatric specialty-specific POCUS curriculum and training to competency have not been defined, POCUS is likely to be most successfully incorporated in clinical care when programmatic infrastructural elements are present. • Risk assessment is a forward-thinking process and requires an imprecise calculus that integrates considerations of the technology, the provider, and the context in which medical care is delivered. Medicolegal considerations vary across countries and frequently change, requiring providers and institutions to understand local regulatory requirements and legal frameworks to mitigate the potential risks of POCUS.
Keywords: Children; Framework; Neonates; Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS); Risk assessment.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Singh Y, Tissot C, Fraga MV, Yousef N, Cortes RG, Lopez J, et al. International evidence-based guidelines on Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) for critically ill neonates and children issued by the POCUS Working Group of the European Society of Paediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) Crit Care. 2020;24(1):65. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Souza TH, Brandão MB, Nadal JAH et al (2018) Ultrasound Guidance for Pediatric Central Venous Catheterization: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 142: e20181719 - PubMed
-
- Hanada S, Van Winkle MT, Subramani S et al (2017) Dynamic ultrasound-guided short-axis needle tip navigation technique vs. landmark technique for difficult saphenous vein access in children: a randomised study. Anaesthesia 72:1508–1515 - PubMed
-
- Takeshita J, Yoshida T, Nakajima Y, et al. Superiority of Dynamic Needle Tip Positioning for Ultrasound-Guided Peripheral Venous Catheterization in Patients Younger Than 2 Years Old: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2019;20:e410–e414. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

