Molecular studies into cell biological role of Copine-4 in Retinal Ganglion Cells
- PMID: 34847148
- PMCID: PMC8631636
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255860
Molecular studies into cell biological role of Copine-4 in Retinal Ganglion Cells
Abstract
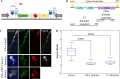
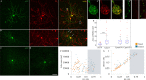
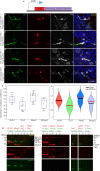
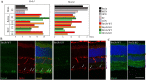
The molecular mechanisms underlying morphological diversity in retinal cell types are poorly understood. We have previously reported that several members of the Copine family of Ca-dependent membrane adaptors are expressed in Retinal Ganglion Cells and transcriptionally regulated by Brn3 transcription factors. Several Copines are enriched in the retina and their over-expression leads to morphological changes -formation of elongated processes-, reminiscent of neurites, in HEK293 cells. However, the role of Copines in the retina is largely unknown. We now investigate Cpne4, a Copine whose expression is restricted to Retinal Ganglion Cells. Over-expression of Cpne4 in RGCs in vivo led to formation of large varicosities on the dendrites but did not otherwise visibly affect dendrite or axon formation. Protein interactions studies using yeast two hybrid analysis from whole retina cDNA revealed two Cpne4 interacting proteins-Host Cell Factor 1 and Morn2. Mass Spectrometry analysis of retina lysate pulled down using Cpne4 or its vonWillebrand A domain showed 207 interacting proteins. A Gene Ontology analysis of the discovered proteins suggests that Cpne4 is involved in several metabolic and signaling pathways in the retina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential expression and subcellular localization of Copines in mouse retina.J Comp Neurol. 2019 Oct 1;527(14):2245-2262. doi: 10.1002/cne.24684. Epub 2019 Mar 28. J Comp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30866042 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic interactions between Brn3 transcription factors in retinal ganglion cell type specification.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 8;8(10):e76347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076347. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116103 Free PMC article.
-
Brn3b/Brn3c double knockout mice reveal an unsuspected role for Brn3c in retinal ganglion cell axon outgrowth.Development. 2002 Jan;129(2):467-77. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.2.467. Development. 2002. PMID: 11807038
-
Intraretinal projection of retinal ganglion cell axons as a model system for studying axon navigation.Brain Res. 2008 Feb 4;1192:165-77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.116. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 17320832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotrophic regulation of retinal ganglion cell synaptic connectivity: from axons and dendrites to synapses.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(8-9):947-56. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041883sc. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15558485 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Age-Related Hearing Loss in CFW Mice Identifies Multiple Genes and Loci, Including Prkag2.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2025 May 21. doi: 10.1007/s10162-025-00994-1. Online ahead of print. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40399499
-
Copines, a Family of Calcium Sensor Proteins and Their Role in Brain Function.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 21;14(3):255. doi: 10.3390/biom14030255. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide association study for age-related hearing loss in CFW mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 10:2024.06.10.598304. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.10.598304. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2025 May 21. doi: 10.1007/s10162-025-00994-1. PMID: 38915500 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Copine A is essential for calcium homeostasis in Dictyostelium.Cell Calcium. 2025 Sep;130:103055. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2025.103055. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Cell Calcium. 2025. PMID: 40706150
-
Copine C plays a role in adhesion and streaming in Dictyostelium.Cell Adh Migr. 2024 Dec;18(1):1-19. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2024.2315629. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Cell Adh Migr. 2024. PMID: 38378453 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

