CXCL10 chemokine regulates heterogeneity of the CD8+ T cell response and viral set point during chronic infection
- PMID: 34847356
- PMCID: PMC8755631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.11.002
CXCL10 chemokine regulates heterogeneity of the CD8+ T cell response and viral set point during chronic infection
Abstract
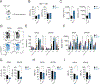
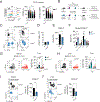
CD8+ T cells responding to chronic infection adapt an altered differentiation program that provides some restraint on pathogen replication yet limits immunopathology. This adaptation is imprinted in stem-like cells and propagated to their progeny. Understanding the molecular control of CD8+ T cell differentiation in chronic infection has important therapeutic implications. Here, we find that the chemokine receptor CXCR3 is highly expressed on viral-specific stem-like CD8+ T cells and that one of its ligands, CXCL10, regulates the persistence and heterogeneity of responding CD8+ T cells in spleens of mice chronically infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. CXCL10 is produced by inflammatory monocytes and fibroblasts of the splenic red pulp, where it grants stem-like cells access to signals promoting differentiation and limits their exposure to pro-survival niches in the white pulp. Consequently, functional CD8+ T cell responses are greater in Cxcl10-/- mice and are associated with a lower viral set point.
Keywords: CD8+ T cells; CXCL10; CXCR3; LCMV; T cell exhaustion; TCF-1; T cell differentiation; chemokine; chronic viral infection.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.R.M is a founder, shareholder, and member of the advisory board of Monopteros Therapeutics, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
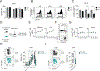




References
-
- Alfei F, Kanev K, Hofmann M, Wu M, Ghoneim HE, Roelli P, Utzschneider DT, von Hoesslin M, Cullen JG, Fan Y, Eisenberg V, Wohlleber D, Steiger K, Merkler D, Delorenzi M, Knolle PA, Cohen CJ, Thimme R, Youngblood B, and Zehn D 2019. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection. Nature 571:265–269. - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, and Ahmed R 2006. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439:682–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

