Obesity, Diabetes, and Increased Cancer Progression
- PMID: 34847640
- PMCID: PMC8640143
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0077
Obesity, Diabetes, and Increased Cancer Progression
Abstract
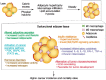
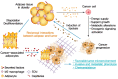
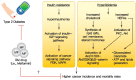
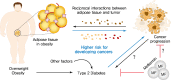
Rates of obesity and diabetes have increased significantly over the past decades and the prevalence is expected to continue to rise further in the coming years. Many observations suggest that obesity and diabetes are associated with an increased risk of developing several types of cancers, including liver, pancreatic, endometrial, colorectal, and post-menopausal breast cancer. The path towards developing obesity and diabetes is affected by multiple factors, including adipokines, inflammatory cytokines, growth hormones, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. The metabolic abnormalities associated with changes in the levels of these factors in obesity and diabetes have the potential to significantly contribute to the development and progression of cancer through the regulation of distinct signaling pathways. Here, we highlight the cellular and molecular pathways that constitute the links between obesity, diabetes, cancer risk and mortality. This includes a description of the existing evidence supporting the obesity-driven morphological and functional alternations of cancer cells and adipocytes through complex interactions within the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: Adipokines; Adipose tissue; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Hyperlipidemia; Insulin resistance; Neoplasms; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Lega IC, Lipscombe LL. Review: diabetes, obesity, and cancerpathophysiology and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 2020;41:bnz014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

