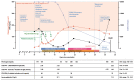
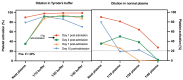
Fatal exacerbation of ChadOx1-nCoV-19-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia syndrome after initial successful therapy with intravenous immunoglobulins - a rational for monitoring immunoglobulin G levels
- PMID: 34847660
- PMCID: PMC8634183
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.279509
Fatal exacerbation of ChadOx1-nCoV-19-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia syndrome after initial successful therapy with intravenous immunoglobulins - a rational for monitoring immunoglobulin G levels
Figures
References
-
- Morel-Kopp MC, Mullier F, Gkalea V, et al. . Heparin-induced multielectrode aggregometry method for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia testing: communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14(12):2548-2552. - PubMed
-
- Robert T. Proposed Brighton Collaboration process for developing a standard case definition for study of new clinical syndrome X, as applied to thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) - V10.16.3. Accessed on May 30, 2021. Available from: https://brightoncollaboration.us/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/TTS-Case-Fin....
-
- Guidance produced from the Expert Hematology Panel (EHP) focused on Covid-19 vaccine induced thrombosis and thrombocytopenia (VITT) updated guidance on management. Version 1.3. Accessed on Apr 7, 2021. Available from: https://b-sh.org.uk/media/19530/guidance-version-13-on-mngmt-of-thrombos....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

