Effect of CYP2C19 polymorphisms on serum valproic level acid in Chinese Han patients with schizophrenia
- PMID: 34848811
- PMCID: PMC8632882
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-02628-x
Effect of CYP2C19 polymorphisms on serum valproic level acid in Chinese Han patients with schizophrenia
Abstract
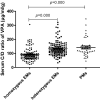
Valproic acid is an anticonvulsant, which is also widely used for treating psychiatric disorders. Some clinical trials have demonstrated benefits of valproic acid augmentation therapy in schizophrenia. Interindividual variability in valproic acid dose and serum concentration may reflect functional consequences of genetic polymorphisms in genes encoding drug-metabolizing enzymes. The aim of this study was to determine the relationship between serum concentrations of valproic acid and single nucleotide polymorphisms of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19 gene in patients with schizophrenia. All patients had been receiving fixed dose of valproic acid for at least 2 weeks. The daily doses were 0.5-1.5 g. No other drugs except olanzapine were coadministered. Serum concentrations of valproic acid were measured using the ultra-high performance liquid chromatography method with mass-spectrometric detection. The CYP2C19 (CYP2C19*2 G681A rs4244285 and CYP2C19*3 G636A rs4986893) genotypes were identified by real-time PCR analyses. The mean concentration/dose ratios of valproic acid were significantly higher in patients with CYP2C19 *1/*2 genotype (P < 0.01) or CYP2C19 *2/*3 genotype (P < 0.01) than in those with CYP2C12 *1/*1 genotype. The mean concentration/dose ratios of valproic acid were significantly higher in patients with 1 (P < 0.01) or 2 (P < 0.01) mutated alleles for CYP2C19 than in those without mutated alleles. And the post hoc analysis revealed that the result has acceptable statistical (power (1 - β) = 0.8486 at type I level of 0.05) to support the observed significant associations for CYP2C19 SNPs and serum C/D ratios of valproic acid. The findings of this study suggest that the genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C19 significantly affect the steady-state serum concentrations of valproic acid in Chinese Han population. The determination of the CYP2C19 genotypes may be useful for dosing adjustment in schizophrenia patients on valproic acid therapy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Citrome L. Schizophrenia and valproate. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 2003;37(Suppl 2):74–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical