The COVOSMIA-19 trial: Preliminary application of the Singapore smell and taste test to objectively measure smell and taste function with COVID-19
- PMID: 34848929
- PMCID: PMC8612753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2021.104482
The COVOSMIA-19 trial: Preliminary application of the Singapore smell and taste test to objectively measure smell and taste function with COVID-19
Abstract
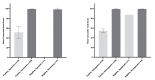
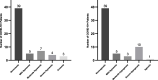
Sudden loss of smell and/or taste has been identified as an early symptom of SARS-CoV-2 2019 (COVID-19) infection, and presents an effective target for prompt self-isolation and reducing community spread. The current study sought to develop and test a novel, rapid, self-administered test to objectively measure smell and taste losses associated with COVID-19, and administered self-report questionnaires to characterise symptoms associated with COVID-19 in Singapore. Participants (N = 99) completed questionnaires to record recent changes in smell and taste ability. This was followed by the 'Singapore Smell and Taste Test' (SSTT), a personal, objective testing kit for daily self-assessment of smell and taste function at their place of residence. Seventy-two recruited participants were confirmed as COVID-19 positive at baseline, of which 58 completed the SSTT at home. Of these, 36.2% had objectively measured smell and/or taste loss. The SSTT measures of smell and taste function were positively associated with participants' self-reported smell and taste acuity, and rated smell intensity of 6 common household items. This study presents the first application of the SSTT as a rapid, cost-effective, objective tool to self-monitor smell and taste function in a residential setting, and ensures comparability across individuals through the use of standardised stimuli. The SSTT has potential for future application in populations with limited access to formal COVID-19 testing as a self-administered objective method to monitor sudden changes in smell and taste, and to prompt early self-isolation, in order to reduce community transmission of COVID-19.
Keywords: Ageusia; Anosmia; COVID-19; COVID-19, Coronavirus disease 2019; Gustatory dysfunction; Olfactory dysfunction; PCR, Polymerase Chain Reaction; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; SNOT-22, 22-item Sino-Nasal Outcome test; SSTQ, The Singapore Smell and Taste Questionnaire; SSTT, The Singapore Smell and Taste Test; VAS, Visual Analogue Scale.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. (2020). Anosmia, Hyposmia, and Dysgeusia Symptoms of Coronavirus Disease. https://www.entnet.org/content/aao-hns-anosmia-hyposmia-and-dysgeusia-sy....
-
- Bagheri S.H., Asghari A., Farhadi M., Shamshiri A.R., Kabir A., Kamrava S.K., Jalessi M., Mohebbi A., Alizadeh R., Honarmand A.A., Ghalehbaghi B., Salimi A., Firouzabadi F.D. Coincidence of COVID-19 epidemic and olfactory dysfunction outbreak in Iran. Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran. 2020;34(1)(62):1–7. doi: 10.34171/mjiri.34.62. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
