Therapeutic Effects and Safe Uses of Plant-Derived Polyphenolic Compounds in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Review
- PMID: 34848944
- PMCID: PMC8619826
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S327238
Therapeutic Effects and Safe Uses of Plant-Derived Polyphenolic Compounds in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Review
Abstract
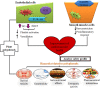
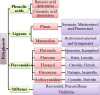
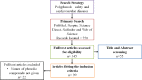
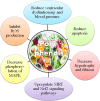
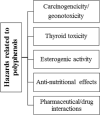
Polyphenols have long been recognized as health-promoting entities, including beneficial effects on cardiovascular disease, but their reputation has been boosted recently following a number of encouraging clinical studies in multiple chronic pathologies, that seem to validate efficacy. Health benefits of polyphenols have been linked to their well-established powerful antioxidant activity. This review aims to provide comprehensive and up-to-date knowledge on the current therapeutic status of polyphenols having sufficient heed towards the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, data about the safety profile of highly efficacious polyphenols has also been investigated to further enhance their role in cardiac abnormalities. Evidence is presented to support the action of phenolic derivatives against cardiovascular pathologies by following receptors and signaling pathways which ultimately cause changes in endogenous antioxidant, antiplatelet, vasodilatory, and anti-inflammatory activities. In addition, in vitro antioxidant and pre-clinical and clinical experiments on anti-inflammatory as well as immunomodulatory attributes of polyphenols have revealed their role as cardioprotective agents. However, an obvious shortage of in vivo studies related to dose selection and toxicity of polyphenols makes these compounds a suitable target for clinical investigations. Further studies are needed for the development of safe and potent herbal products against cardiovascular diseases. The novelty of this review is to provide comprehensive knowledge on polyphenols safety and their health claims. It will help researchers to identify those moieties which likely exert protective and therapeutic effects towards cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: antioxidant; cardioprotective; cardiovascular diseases; clinical trials; polyphenols.
© 2021 Alotaibi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Lopez EO, Ballard BD, Jan A. Cardiovascular Disease. StatPearls; 2020. - PubMed
-
- Nazon E. An overview of cardiovascular disease and research. WR-467-RS; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

