Data Mining of Free-Text Responses: An Innovative Approach to Analyzing Patient Perspectives on Treatment for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps in a Phase IIa Proof-of-Concept Study for Dupilumab
- PMID: 34848949
- PMCID: PMC8611726
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S320242
Data Mining of Free-Text Responses: An Innovative Approach to Analyzing Patient Perspectives on Treatment for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps in a Phase IIa Proof-of-Concept Study for Dupilumab
Abstract
Purpose: Patient perspective is an important and increasingly sought-after complement to clinical assessment. The aim of this study was to transcribe individual patients' experience of treatment in a dupilumab clinical trial through free-text responses with analysis using natural language processing (NLP) to obtain the unique perspective of patients on disease impact and unmet needs with existing treatment to inform future trial design.
Patients and methods: Patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) who were enrolled in a Phase IIa randomized controlled trial comparing dupilumab with placebo (NCT01920893) were invited to complete a self-assessment of treatment (SAT) tool at the end of treatment, asking, "What is your opinion on the treatment you had during the trial? What did you like or dislike about the treatment?" Free-text responses were analyzed for the overall cohort and according to treatment assignment using natural language processing including sentiment scoring. In a mixed-methods approach, quantitative patient-reported outcome (PRO) results were utilized to complement the qualitative analysis of free-text responses.
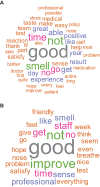
Results: Of 60 patients enrolled in the study, 43 (71.6%) completed the SAT and responses from 37 patients were analyzed (placebo, n = 16; dupilumab, n = 21). Word analyses showed that the most common words were "smell," "improve," "staff," "great," "time," and "good." Across the whole cohort, "smell" was the most common symptom-related word. The words "smell" and "experience" were more likely to occur in patients treated with dupilumab. Patients treated with dupilumab also had more positive sentiment in their SAT responses than those who received placebo. The results from this qualitative analysis were reflected in quantitative PRO results.
Conclusion: "Smell" was important to patients with CRSwNP, highlighting its importance as a patient-centric efficacy outcome measure in the context of clinical trials in CRSwNP.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01920893. Registered 12 August 2013, https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01920893.
Keywords: CRSwNP; free-text data mining; patient perspective; self-assessment; sense of smell.
© 2021 Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AHK, PC, LPM, PM, and LE are employees of Sanofi, and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. AA, MR, and GP are former employees of Sanofi. JC and NA are employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and shareholders in the company. BF is a consultant for AbbVie, Actelion, Allergan, Almirall, Alnylam, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biocodex, Biogen, Biopecs, Bioprojet, Biotronik, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgène, Chiesi, D&A Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Ethypharm, Genevrier, Genzyme, Gilead, Grunenthal, GSK, HRA, IDM Pharma, Idorsia, Indivior, Janssen, Lundbeck, Léo, Menarini, Novonordisk, MSD, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Recordati, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, Stallergenes Greer, Takeda, UCB, and ViiV. CB is an advisory board member for ALK, ASIT Biotech, AstraZeneca, Intrexon Actobiotics, Novartis, Sanofi, and Stallergenes Greer. JM is a member of national or international advisory boards, and received speaker fees or funding for clinical trials and research projects from ALK, AstraZeneca, Genentech, GSK, Glenmark, Menarini, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, MSD, Mylan-MEDA Pharma, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sanofi Genzyme, UCB Pharma, and Uriach Group. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Halpern J. From Detached Concern to Empathy: Humanizing Medical Practice. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2001.
-
- Messina J, Grainger DL. A pilot study to identify areas for further improvements in patient and public involvement in health technology assessments for medicines. Patient. 2012;5(3):199–211. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

