Relationship Between an Ischaemic J Wave Pattern and Ventricular Fibrillation in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients
- PMID: 34849013
- PMCID: PMC8627274
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S337638
Relationship Between an Ischaemic J Wave Pattern and Ventricular Fibrillation in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients
Abstract
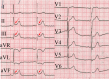
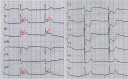
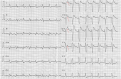
Background: This study determined the ischaemic J wave pattern associated with ventricular fibrillation (VF).
Methods: A total of 262 patients diagnosed with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) were recruited from October 2017 to September 2020. All data were collected and analysed, including baseline characteristics, electrocardiogram (ECG), coronary angiography (CAG), and examination outcomes.
Results: There were 193 STEMI patients with J wave elevation but without an ischaemic J wave (NJ group) and 69 patients with an ischaemic J wave; the latter were then subgrouped into early repolarization pattern (ERP; n=62) and Brugada pattern groups (BrP [anteroseptal ERP]; n=7). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to clarify high-risk factors and characteristics of ischaemic J waves. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that an ischaemic J wave (odds ratio [OR], 9.708; 95% CI, 2.570-36.664; P=0.01) independently predicted VF. In the subgroup analysis, BrP (OR, 31.214; 95% CI, 3.949-246.742; P=0.001), slur morphology of the ERP (OR, 8.15; 95% CI, 1.563-42.558; P<0.05), and the number of leads with an ischaemic J wave > 3 (OR, 16.174; 95% CI, 3.064-85.375; P=0.001) were significantly associated with VF occurrence after adjusting for multiple variables.
Conclusion: An ischaemic J wave is an independent risk factor for VF in STEMI patients. BrP, slur morphology, and > 3 leads with an ischaemic J wave could increase the incidence of VF.
Keywords: STEMI; classification; ischaemic J wave; predictor; ventricular fibrillation.
© 2021 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Shipley RA, Hallaran WR. The four lead electrocardiogram in 200 normal men and women. Am Heart J. 1936;11:325–345. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8703(36)90417-9 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

