Endothelial ARHGEF26 is an angiogenic factor promoting VEGF signalling
- PMID: 34849650
- PMCID: PMC9586566
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvab344
Endothelial ARHGEF26 is an angiogenic factor promoting VEGF signalling
Abstract
Aims: Genetic studies have implicated the ARHGEF26 locus in the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). However, the causal pathways by which DNA variants at the ARHGEF26 locus confer risk for CAD are incompletely understood. We sought to elucidate the mechanism responsible for the enhanced risk of CAD associated with the ARHGEF26 locus.
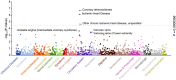
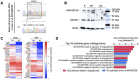
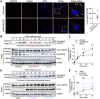
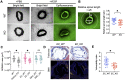
Methods and results: In a conditional analysis of the ARHGEF26 locus, we show that the sentinel CAD-risk signal is significantly associated with various non-lipid vascular phenotypes. In human endothelial cell (EC), ARHGEF26 promotes the angiogenic capacity, and interacts with known angiogenic factors and pathways. Quantitative mass spectrometry showed that one CAD-risk coding variant, rs12493885 (p.Val29Leu), resulted in a gain-of-function ARHGEF26 that enhances proangiogenic signalling and displays enhanced interactions with several proteins partially related to the angiogenic pathway. ARHGEF26 is required for endothelial angiogenesis by promoting macropinocytosis of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR2) on cell membrane and is crucial to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-dependent murine vessel sprouting ex vivo. In vivo, global or tissue-specific deletion of ARHGEF26 in EC, but not in vascular smooth muscle cells, significantly reduced atherosclerosis in mice, with enhanced plaque stability.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that ARHGEF26 is involved in angiogenesis signaling, and that DNA variants within ARHGEF26 that are associated with CAD risk could affect angiogenic processes by potentiating VEGF-dependent angiogenesis.
Keywords: angiogenesis; atherosclerosis; coronary artery disease; endothelial cell.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2021. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: P.E. has received sponsored research support from Bayer AG and IBM Health. He has also served on advisory boards or consulted for Bayer AG, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia and Novartis. T.M. and S.K. are employees of Verve Therapeutics. S.K. holds equity in Verve Therapeutics, Maze Therapeutics, Catabasis, and San Therapeutics. He is a member of the scientific advisory boards for Regeneron Genetics Center and Corvidia Therapeutics; he has served as a consultant for Acceleron, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Novo Ventures, Ionis, Alnylam, Aegerion, Haug Partners, Noble Insights, Leerink Partners, Bayer Healthcare, Illumina, Colour Genomics, MedGenome, Quest, and Medscape; he reports patents related to a method of identifying and treating a person having a predisposition to or afflicted with cardiometabolic disease (20180010185) and a genetics risk predictor (20190017119).
Figures



Comment in
-
ARHGEF26: a new player in vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 trafficking.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Oct 21;118(13):2735-2736. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac149. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 36103599 No abstract available.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Das SR, Delling FN, Djousse L, Elkind MSV, Ferguson JF, Fornage M, Jordan LC, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Kwan TW, Lackland DT, Lewis TT, Lichtman JH, Longenecker CT, Loop MS, Lutsey PL, Martin SS, Matsushita K, Moran AE, Mussolino ME, O'Flaherty M, Pandey A, Perak AM, Rosamond WD, Roth GA, Sampson UKA, Satou GM, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Spartano NL, Stokes A, Tirschwell DL, Tsao CW, Turakhia MP, VanWagner LB, Wilkins JT, Wong SS, Virani SS; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee . Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: a Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019;139:e56–e528. - PubMed
-
- Erdmann J, Kessler T, Munoz Venegas L, Schunkert H.. A decade of genome-wide association studies for coronary artery disease: the challenges ahead. Cardiovasc Res 2018;114:1241–1257. - PubMed
-
- Musunuru K, Kathiresan S.. Genetics of common, complex coronary artery disease. Cell 2019;177:132–145. - PubMed
-
- Nelson CP, Goel A, Butterworth AS, Kanoni S, Webb TR, Marouli E, Zeng L, Ntalla I, Lai FY, Hopewell JC, Giannakopoulou O, Jiang T, Hamby SE, Di Angelantonio E, Assimes TL, Bottinger EP, Chambers JC, Clarke R, Palmer CNA, Cubbon RM, Ellinor P, Ermel R, Evangelou E, Franks PW, Grace C, Gu D, Hingorani AD, Howson JMM, Ingelsson E, Kastrati A, Kessler T, Kyriakou T, Lehtimaki T, Lu X, Lu Y, Marz W, McPherson R, Metspalu A, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Ruusalepp A, Schadt EE, Schmidt AF, Sweeting MJ, Zalloua PA, AlGhalayini K, Keavney BD, Kooner JS, Loos RJF, Patel RS, Rutter MK, Tomaszewski M, Tzoulaki I, Zeggini E, Erdmann J, Dedoussis G, Bjorkegren JLMEpic-CVD Consortium; CardioGramplusC4D; UK Biobank CardioMetabolic CHD Working Group Schunkert H, Farrall M, Danesh J, Samani NJ, Watkins H, Deloukas P.. Association analyses based on false discovery rate implicate new loci for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet 2017;49:1385–1391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

