Emergency rollout and conversion procedures during the three-arm robotic open-thoracotomy-view approach
- PMID: 34849975
- PMCID: PMC9159417
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivab336
Emergency rollout and conversion procedures during the three-arm robotic open-thoracotomy-view approach
Abstract
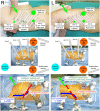
Objectives: To conduct robotic lung resections (RLRs) with views similar to those in open-thoracotomy surgery (OTS), we adopted a vertical port placement and confronting upside-down monitor setting: the robotic open-thoracotomy-view approach (OTVA). We herein discuss the procedures for emergency rollout and conversion from the robotic OTVA to OTS or video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS).
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the cases of 88 patients who underwent RLR with three-arm OTVA using the da Vinci Xi Surgical System between February 2019 and July 2021. Robotic ports were vertically placed along the axillary line, and 2 confronting monitors and 2 assistants were positioned on each side of the patient. Three possible conversions were prepared: (i) emergency thoracotomy using an incision along the ribs in a critical situation, (ii) cool conversion using vertical incision thoracotomy in a calmer condition and (iii) conversion to confronting VATS. All staff involved in the surgery repeatedly rehearsed the emergency rollout in practice.
Results: No emergent or cool conversion to OTS occurred. Two patients (2.3%) experienced confronting VATS conversions. One patient underwent an urgent conversion for a moderate haemorrhage from a pulmonary artery branch during left upper lobectomy in the introduction phase. Another patient underwent a calmer conversion during an extended RS6 + S10a segmentectomy, where staples could not be inserted appropriately due to lung lacerations. In all patients, postoperative courses were uneventful.
Conclusions: The OTVA setting is a possible option for RLRs. This report describes the emergent rollout and subsequent conversion procedures for this method.
Keywords: Confronting monitors; Emergency rollout and conversion procedures; Open-thoracotomy-view approach; Robotic lung resection; Vertical port placement.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.
Figures


Comment in
-
Robotic development: 'patients' safety always comes first'.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2022 Jun 1;34(6):1052-1053. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivac057. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2022. PMID: 35356982 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cerfolio RJ, Bess KM, Wei B, Minnich DJ.. Incidence, results, and our current intraoperative technique to control major vascular injuries during minimally invasive robotic thoracic surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 2016;102:394–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

