Accurate expression quantification from nanopore direct RNA sequencing with NanoCount
- PMID: 34850115
- PMCID: PMC8886870
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab1129
Accurate expression quantification from nanopore direct RNA sequencing with NanoCount
Abstract
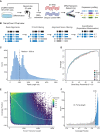
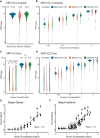
Accurately quantifying gene and isoform expression changes is essential to understanding cell functions, differentiation and disease. Sequencing full-length native RNAs using long-read direct RNA sequencing (DRS) has the potential to overcome many limitations of short and long-read sequencing methods that require RNA fragmentation, cDNA synthesis or PCR. However, there are a lack of tools specifically designed for DRS and its ability to identify differential expression in complex organisms is poorly characterised. We developed NanoCount for fast, accurate transcript isoform quantification in DRS and demonstrate it outperforms similar methods. Using synthetic controls and human SH-SY5Y cell differentiation into neuron-like cells, we show that DRS accurately quantifies RNA expression and identifies differential expression of genes and isoforms. Differential expression of 231 genes, 333 isoforms, plus 27 isoform switches were detected between undifferentiated and differentiated SH-SY5Y cells and samples clustered by differentiation state at the gene and isoform level. Genes upregulated in neuron-like cells were associated with neurogenesis. NanoCount quantification of thousands of novel isoforms discovered with DRS likewise enabled identification of their differential expression. Our results demonstrate enhanced DRS isoform quantification with NanoCount and establish the ability of DRS to identify biologically relevant differential expression of genes and isoforms.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Utilizing Nanopore direct RNA sequencing of blood from patients with sepsis for discovery of co- and post-transcriptional disease biomarkers.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 May 13;25(1):692. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11078-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40355874 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic benchmark of Nanopore long-read RNA sequencing for transcript-level analysis in human cell lines.Nat Methods. 2025 Apr;22(4):801-812. doi: 10.1038/s41592-025-02623-4. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 40082608 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore guided annotation of transcriptome architectures.mSystems. 2024 Jul 23;9(7):e0050524. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00505-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38953320 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing novel isoform discovery: leveraging nanopore long-read sequencing and machine learning approaches.Brief Funct Genomics. 2024 Dec 6;23(6):683-694. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elae031. Brief Funct Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39158328 Review.
-
Charting the epitranscriptomic landscape across RNA biotypes using native RNA nanopore sequencing.Mol Cell. 2025 Jan 16;85(2):276-289. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.12.014. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Mol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39824168 Review.
Cited by
-
The Long and the Short of It: NEAT1 and Cancer Cell Metabolism.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 9;14(18):4388. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184388. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DELongSeq for efficient detection of differential isoform expression from long-read RNA-seq data.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023 Mar 3;5(1):lqad019. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad019. eCollection 2023 Mar. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 36879902 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense lncRNA CHROMR is linked to glioma patient survival.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Mar 6;10:1101953. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1101953. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36950523 Free PMC article.
-
NMDtxDB: data-driven identification and annotation of human NMD target transcripts.RNA. 2024 Sep 16;30(10):1277-1291. doi: 10.1261/rna.080066.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 39095083 Free PMC article.
-
Toward the use of nanopore RNA sequencing technologies in the clinic: challenges and opportunities.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 27;53(5):gkaf128. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf128. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40057374 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pan Q., Shai O., Lee L.J., Frey B.J., Blencowe B.J.. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2008; 40:1413–1415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/J004669/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 201879/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BRC-1215-20005/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/T/000PR9817/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P026028/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

