Intracerebral Proinflammatory Cytokine Increase in Surgically Evacuated Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Microdialysis Study
- PMID: 34850333
- PMCID: PMC9110446
- DOI: 10.1007/s12028-021-01389-9
Intracerebral Proinflammatory Cytokine Increase in Surgically Evacuated Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Microdialysis Study
Abstract
Background: Treatment options for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) are limited. A possible inflammatory response in the brain tissue surrounding an ICH may exacerbate the initial injury and could be a target for treatment of subsequent secondary brain injury. The study objective was to compare levels of inflammatory mediators in the interstitial fluid of the perihemorrhagic zone (PHZ) and in seemingly normal cortex (SNX) in the acute phase after surgical evacuation of ICH, with the hypothesis being that a difference could be demonstrated between the PHZ and the SNX.
Methods: In this observational study, ten patients needing surgical evacuation of supratentorial ICH received two cerebral microdialysis catheters: one in the PHZ and one in the SNX that is remote from the ICH. The microdialysate was analyzed for energy metabolites (including lactate pyruvate ratio and glucose) and for inflammatory mediators by using a multiplex immunoassay of 27 cytokines and chemokines at 6-10 h, 20-26 h, and 44-50 h after surgery.
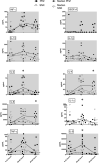
Results: A metabolic crisis, indicated by altered energy metabolic markers, that persisted throughout the observation period was observed in the PHZ when compared with the SNX. Proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL) 8, tumor necrosis factor α, IL-2, IL-1β, IL-6 and interferon γ, anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-13, IL-4, and vascular endothelial growth factor A were significantly higher in PHZ compared with SNX and were most prominent at 20-26 h following ICH evacuation.
Conclusions: Higher levels of both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the perihemorrhagic brain tissue implies a complex role for inflammatory mediators in the secondary injury cascades following ICH surgery, suggesting a need for targeted pharmacological interventions.
Keywords: Brain injury; Cytokine; Inflammation mediators; Intracranial hemorrhage; Microdialysis; Stroke.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hemphill JC, 3rd, Greenberg SM, Anderson CS, et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke J Cereb Circ. 2015;46:2032–2060. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000069. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Rowan EN, Murray GD, Gholkar A, Mitchell PM. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial lobar intracerebral haematomas (STICH II): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2013;382:397–408. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60986-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prasad K, Mendelow AD, Gregson B. Surgery for primary supratentorial intracerebral haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008; Cd000200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

