Clinical outcome, long-term survival and tolerability of sequential therapy of first-line crizotinib followed by alectinib in advanced ALK+NSCLC: A multicenter retrospective analysis in China
- PMID: 34851035
- PMCID: PMC8720624
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14232
Clinical outcome, long-term survival and tolerability of sequential therapy of first-line crizotinib followed by alectinib in advanced ALK+NSCLC: A multicenter retrospective analysis in China
Abstract
Background: There is limited data on the clinical outcome, long-term survival and tolerability of sequential therapy of first-line crizotinib followed by alectinib in a real-world setting for Chinese patients with advanced ALK+ NSCLC.
Methods: The medical records of patients who received sequential therapy with first-line crizotinib followed by alectinib (no intermittent systemic therapy was allowed between the two ALK-TKIs) were collected from six centers in China. Combined time treatment to failure (C-TTF) was defined as the period from the start of crizotinib to the complete discontinuation of alectinib due to any cause.
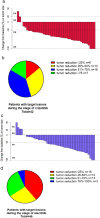
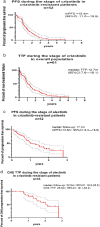
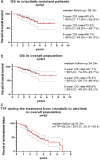
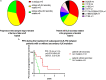
Results: A total of 61 patients were included in our study. Fifty-two patients were switched to alectinib due to disease progression, seven as a result of toxicity, and two due to patient preference. At the time of data cutoff, alectinib treatment was discontinued in 31 patients on account of disease progression while severe adverse events resulted in cessation of alectinib in another two patients. Rebiopsy was conducted in 21 patients following disease progression on alectinib in whom ALK secondary mutation was found in 13 patients. Patients with ALK secondary mutation demonstrated better PFS during treatment with subsequent ALK-TKIs compared with those without (10.4 vs. 3.1 m, p = 0.0018, HR = 0.08). With a median follow-up of 34.3 months, C-TTF was 39.2 months and estimated 5-year OS was 68.6% in the overall population.
Conclusion: Sequential therapy with first-line crizotinib followed by alectinib demonstrated long-term benefits. Different efficacy in subsequent ALK-TKI between patients with or without ALK secondary mutation further emphasized the importance of rebiopsy to guide targeted therapy more precisely.
Keywords: ALK+ NSCLC; Alectinib; Crizotinib.
© 2021 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors report any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment Sequencing in Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan: A Real-World Observational Study.Adv Ther. 2020 Jul;37(7):3311-3323. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01392-0. Epub 2020 May 29. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32472430
-
Progression-Free and Overall Survival of Patients With ALK Rearrangement-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated Sequentially With Crizotinib and Alectinib.Clin Lung Cancer. 2016 Nov;17(6):528-534. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 18. Clin Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27318655
-
Sequential therapy of crizotinib followed by alectinib for non-small cell lung cancer harbouring anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement (WJOG9516L): A multicenter retrospective cohort study.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Mar;145:183-193. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.12.026. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33486442
-
Effect of alectinib versus crizotinib on progression-free survival, central nervous system efficacy and adverse events in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 Jul;9(4):1782-1796. doi: 10.21037/apm-19-643. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32527124
-
Mixed responses to first-line alectinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients with rare ALK gene fusions: A case series and literature review.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(19):9476-9481. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16897. Epub 2021 Sep 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34541785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathological complete remission in ALK-positive lung cancer patient after multiple lines of conversion therapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 29;12:967675. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.967675. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36523965 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Alectinib/Crizotinib Data in First-Line Therapy in Patients with Anaplastic LymphomakinasePositive Nonsmall Cell Lung Carcinoma with Poor Prognostic Features for Alectinib.Thorac Res Pract. 2023 Jul;24(4):180-185. doi: 10.5152/ThoracResPract.2023.22200. Thorac Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37485706 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential therapy with crizotinib and a second-generation ALK inhibitor versus direct therapy of a second-generation ALK inhibitor in ALK-positive advanced lung cancer: a real-world study.J Thorac Dis. 2023 May 30;15(5):2425-2437. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1783. Epub 2023 Apr 7. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37324060 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of metastatic ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: real-world outcomes in a single center study.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):2918-2933. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-396. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39670024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Peters S, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Gadgeel S, Ahn JS, Kim DW, et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:829–38. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Mekhail T, et al. First‐line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK‐positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2167–77. - PubMed
-
- Soria J‐C, Tan DSW, Chiari R, Wu YL, Paz‐Ares L, Wolf J, et al. First‐line ceritinib versus platinum‐based chemotherapy in advanced ALK ‐rearranged non‐small‐cell lung cancer (ASCEND‐4): a randomised, open‐label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2017;389:917–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

