Roles of ESCRT Proteins ALIX and CHMP4A and Their Interplay with Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15 during Tick-Borne Flavivirus Infection
- PMID: 34851141
- PMCID: PMC8826915
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01624-21
Roles of ESCRT Proteins ALIX and CHMP4A and Their Interplay with Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15 during Tick-Borne Flavivirus Infection
Abstract
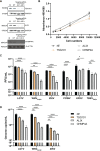
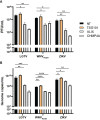
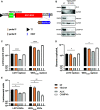
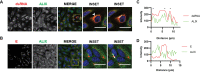
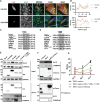
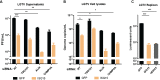
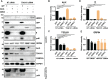
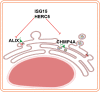
Flaviviruses are usually transmitted to humans via mosquito or tick bites. During infection, virus replication and assembly, whose cellular sites are relatively close, are controlled by virus proteins and a diverse range of host proteins. By siRNA-mediated gene silencing, we showed that ALIX and CHMP4A, two members of the host endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) protein machinery, are required during flavivirus infection. Using cell lines expressing subgenomic replicons and replicon virus-like particles, we demonstrated specific roles for ALIX and CHMP4A in viral replication and assembly, respectively. Employing biochemical and imaging methodology, we showed that the ESCRT proteins are recruited by a putative specific late (L) domain motif LYXLA within the NS3 protein of tick-borne flaviviruses. Furthermore, to counteract the recruitment of ESCRT proteins, the host cells may elicit defense mechanisms. We found that ectopic expression of the interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) or the E3 ISG15-protein ligase (HERC5) reduced virus replication by suppressing the positive effects of ALIX and CHMP4A. Collectively, these results have provided new insights into flavivirus-host cell interactions that function as checkpoints, including the NS3 and the ESCRT proteins, the ISG15 and the ESCRT proteins, at essential stages of the virus life cycle. IMPORTANCE Flaviviruses are important zoonotic viruses with high fatality rates worldwide. Here, we report that during infection, the virus employs members of ESCRT proteins for virus replication and assembly. Among the ESCRT proteins, ALIX acts during virus replication, while CHMP4A is required during virus assembly. Another important ESCRT protein, TSG101, is not required for virus production. The ESCRT, complex, ALIX-CHMP4A, is recruited to NS3 through their interactions with the putative L domain motif of NS3, while CHMP4A is recruited to E. In addition, we demonstrate the antiviral mechanism of ISG15 and HERC5, which degrades ALIX and CHIMP4A, indirectly targets virus infection. In summary, we reveal host-dependency factors supporting flavivirus infection, but these factors may also be targeted by antiviral host effector mechanisms.
Keywords: ALIX; CHMP4A; ESCRT; HERC5; ISG15; NS3; TSG101; assembly; envelope; replication; replicons; tick-borne flaviviruses; virus late domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alix-Mediated Rescue of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Budding Differs from That Observed with Human Immunodeficiency Virus.J Virol. 2020 May 18;94(11):e02019-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02019-19. Print 2020 May 18. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32213612 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 production requires a functional ESCRT-III complex but is independent of TSG101 and ALIX expression.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(21):11254-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00574-09. Epub 2009 Aug 19. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19692479 Free PMC article.
-
The ESCRT-associated protein Alix recruits the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 to facilitate HIV-1 release through the LYPXnL L domain motif.J Virol. 2010 Aug;84(16):8181-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00634-10. Epub 2010 Jun 2. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20519395 Free PMC article.
-
ESCRT machinery and virus infection.Antiviral Res. 2024 Jan;221:105786. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105786. Epub 2023 Dec 24. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 38147902 Review.
-
Role of RNA-binding proteins during the late stages of Flavivirus replication cycle.Virol J. 2020 Apr 25;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01329-7. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32334603 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the function of ESCRT complex and LBPA in ASFV infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Dec 6;13:1163569. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1163569. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38125905 Free PMC article.
-
HRS Facilitates Newcastle Disease Virus Replication in Tumor Cells by Promoting Viral Budding.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 19;25(18):10060. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810060. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337546 Free PMC article.
-
MITD1 is a brain-specific interferon-inducible factor that inhibits flavivirus replication.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 25;122(12):e2502064122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2502064122. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40112111 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the human taste receptor interactome: machine learning and molecular modelling insights into protein-protein interactions.NPJ Sci Food. 2025 Jul 1;9(1):113. doi: 10.1038/s41538-025-00478-9. NPJ Sci Food. 2025. PMID: 40595706 Free PMC article.
-
The Yin and the Yang of extracellular vesicles during viral infections.Biomed J. 2024 Oct;47(5):100659. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100659. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Biomed J. 2024. PMID: 37690583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

