ATF6-Mediated Unfolded Protein Response Facilitates Adeno-associated Virus 2 (AAV2) Transduction by Releasing the Suppression of the AAV Receptor on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
- PMID: 34851146
- PMCID: PMC8826799
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01103-21
ATF6-Mediated Unfolded Protein Response Facilitates Adeno-associated Virus 2 (AAV2) Transduction by Releasing the Suppression of the AAV Receptor on Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Abstract
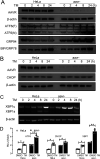
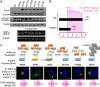
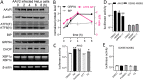
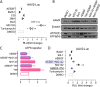
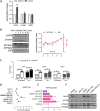
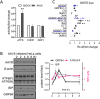
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is extensively used as a viral vector to deliver therapeutic genes during human gene therapy. A high-affinity cellular receptor (AAVR) for most serotypes was recently identified; however, its biological function as a gene product remains unclear. In this study, we used AAVR knockdown cell models to show that AAVR depletion significantly attenuated cells to activate unfolded protein response (UPR) pathways when exposed to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inducer, tunicamycin. By analyzing three major UPR pathways, we found that ATF6 signaling was most affected in an AAVR-dependent fashion, distinct from CHOP and XBP1 branches. AAVR capacity in UPR regulation required the full native AAVR protein, and AAV2 capsid binding to the receptor altered ATF6 dynamics. Conversely, the transduction efficiency of AAV2 was associated with changes in ATF6 signaling in host cells following treatment with different small molecules. Thus, AAVR served as an inhibitory molecule to repress UPR responses via a specificity for ATF6 signaling, and the AAV2 infection route involved the release from AAVR-mediated ATF6 repression, thereby facilitating viral intracellular trafficking and transduction. IMPORTANCE The native function of the AAVR as an ER-Golgi localized protein is largely unknown. We showed that AAVR acted as a functional molecule to regulate UPR signaling under induced ER stress. AAVR inhibited the activation of the transcription factor, ATF6, whereas receptor binding to AAV2 released the suppression effects. This finding has expanded our understanding of AAV infection biology in terms of the physiological properties of AAVR in host cells. Importantly, our research provides a possible strategy which may improve the efficiency of AAV-mediated gene delivery during gene therapy.
Keywords: AAV receptor; AAV transduction; ATF6 signal; UPR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An essential receptor for adeno-associated virus infection.Nature. 2016 Feb 4;530(7588):108-12. doi: 10.1038/nature16465. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26814968 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the cellular unfolded protein response by recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053845. Epub 2013 Jan 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23320106 Free PMC article.
-
Adeno-associated virus 2 bound to its cellular receptor AAVR.Nat Microbiol. 2019 Apr;4(4):675-682. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0356-7. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Nat Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30742069
-
Structural and cellular biology of adeno-associated virus attachment and entry.Adv Virus Res. 2020;106:39-84. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2020.01.002. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Adv Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32327148 Review.
-
Coronavirus-induced ER stress response and its involvement in regulation of coronavirus-host interactions.Virus Res. 2014 Dec 19;194:110-23. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 25304691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nano-hydroxyapatite promotes cell apoptosis by co-activating endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria damage to inhibit glioma growth.Regen Biomater. 2024 Apr 18;11:rbae038. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae038. eCollection 2024. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38799701 Free PMC article.
-
Casein kinase 2 activity is a host restriction factor for AAV transduction.Mol Ther. 2024 Jan 3;32(1):84-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.11.010. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 37952087 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

