Long-term cardiovascular complications following sepsis: is senescence the missing link?
- PMID: 34851467
- PMCID: PMC8636544
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-021-00937-y
Long-term cardiovascular complications following sepsis: is senescence the missing link?
Abstract
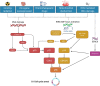
Among the long-term consequences of sepsis (also termed "post-sepsis syndrome") the increased risk of unexplained cardiovascular complications, such as myocardial infarction, acute heart failure or stroke, is one of the emerging specific health concerns. The vascular accelerated ageing also named premature senescence is a potential mechanism contributing to atherothrombosis, consequently leading to cardiovascular events. Indeed, vascular senescence-associated major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) are a potential feature in sepsis survivors and of the elderly at cardiovascular risk. In these patients, accelerated vascular senescence could be one of the potential facilitating mechanisms. This review will focus on premature senescence in sepsis regardless of age. It will highlight and refine the potential relationships between sepsis and accelerated vascular senescence. In particular, key cellular mechanisms contributing to cardiovascular events in post-sepsis syndrome will be highlighted, and potential therapeutic strategies to reduce the cardiovascular risk will be further discussed.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Sepsis; Septic shock; Stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS).
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Septic shock as a trigger of arterial stress-induced premature senescence: A new pathway involved in the post sepsis long-term cardiovascular complications.Vascul Pharmacol. 2021 Dec;141:106922. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2021.106922. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Vascul Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34592427
-
Sepsis Care Pathway 2019.Qatar Med J. 2019 Nov 7;2019(2):4. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2019.qccc.4. eCollection 2019. Qatar Med J. 2019. PMID: 31763206 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms and cardiovascular implications of cancer therapy-induced senescence.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 May;221:107751. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107751. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33275998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Who Have Survived Sepsis: A Nationwide Cohort Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Feb 10;6(2):e004613. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004613. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28188252 Free PMC article.
-
Association between sepsis survivorship and long-term cardiovascular outcomes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Intensive Care Med. 2021 Sep;47(9):931-942. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06479-y. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Intensive Care Med. 2021. PMID: 34373953
Cited by
-
Enhancing sepsis management: the role of dynamic heparin-binding protein monitoring in elderly patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 11;12:1538515. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1538515. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40568199 Free PMC article.
-
How are Long-Covid, Post-Sepsis-Syndrome and Post-Intensive-Care-Syndrome related? A conceptional approach based on the current research literature.Crit Care. 2024 Aug 29;28(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05076-x. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39210399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Coronary Artery Disease in Sepsis Survivors.Biomedicines. 2025 May 13;13(5):1181. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051181. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40427008 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of senescence in critically ill patients: mechanisms, consequences and therapeutic opportunities.Ann Intensive Care. 2024 Jan 5;14(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13613-023-01236-4. Ann Intensive Care. 2024. PMID: 38180573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the performance of genetic risk score for stratifying risk of post-sepsis cardiovascular complications.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 28;10:1076745. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1076745. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36926049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clere-Jehl R, Mariotte A, Meziani F, Bahram S, Georgel P, Helms J. JAK-STAT targeting offers novel therapeutic opportunities in sepsis. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(11):987–1002. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart K, Daniels R, Kissoon N, Machado FR, Schachter RD, Finfer S. Recognizing sepsis as a global health priority—a WHO resolution. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):414–417. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

