Live attenuated virus vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern B.1.1.7 (Alpha) and B.1.351 (Beta)
- PMID: 34851677
- PMCID: PMC8635430
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abk0172
Live attenuated virus vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern B.1.1.7 (Alpha) and B.1.351 (Beta)
Abstract
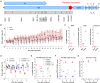
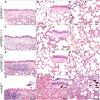
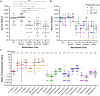
Vaccines are instrumental and indispensable in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. Several recent SARS-CoV-2 variants are more transmissible and evade infection- or vaccine-induced protection. We constructed live attenuated vaccine candidates by large-scale recoding of the SARS-CoV-2 genome and showed that the lead candidate, designated sCPD9, protects Syrian hamsters from a challenge with ancestral virus. Here, we assessed immunogenicity and protective efficacy of sCPD9 in the Roborovski dwarf hamster, a nontransgenic rodent species that is highly susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 and severe COVID-19–like disease. We show that a single intranasal vaccination with sCPD9 elicited strong cross-neutralizing antibody responses against four current SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, B.1.1.7 (Alpha), B.1.351 (Beta), B.1.1.28.1 (Gamma), and B.1.617.2 (Delta). The sCPD9 vaccine offered complete protection from COVID-19–like disease caused by the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1 and the two variants of concern B.1.1.7 and B.1.351.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Live-attenuated vaccine sCPD9 elicits superior mucosal and systemic immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants in hamsters.Nat Microbiol. 2023 May;8(5):860-874. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01352-8. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Nat Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37012419 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal delivery of a chimpanzee adenovirus vector expressing a pre-fusion spike (BV-AdCoV-1) protects golden Syrian hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 3;12:979641. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.979641. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36405962 Free PMC article.
-
A Live Attenuated COVID-19 Candidate Vaccine for Children: Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Challenge in Hamsters.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 24;11(2):255. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020255. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851133 Free PMC article.
-
Development of safe and highly protective live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates by genome recoding.Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 3;36(5):109493. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109493. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34320400 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetically recoded virus sCPD9 - A tool to accelerate SARS-CoV-2 research under biosafety level 2 conditions.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:4376-4380. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.027. Epub 2022 Aug 13. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35992535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural network-assisted humanisation of COVID-19 hamster transcriptomic data reveals matching severity states in human disease.EBioMedicine. 2024 Oct;108:105312. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105312. Epub 2024 Sep 23. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39317638 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 virus lacking the envelope and membrane open-reading frames as a vaccine platform.Nat Commun. 2025 May 14;16(1):4453. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59533-4. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40360482 Free PMC article.
-
An intranasal live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine limits virus transmission.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 2;15(1):995. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45348-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38307868 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse genetics systems for SARS-CoV-2: Development and applications.Virol Sin. 2023 Dec;38(6):837-850. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Virol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37832720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Infection of Omicron BA.5.2 in Patients Provides Broad Immune Responses Against SARS-CoV-2.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 26;13(4):746. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040746. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, Draft landscape of COVID-19 candidate vaccines (2021); https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-cand....
-
- Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency, UK medicines regulator gives approval for first UK COVID-19 vaccine (2020); https://www.gov.uk/government/news/uk-medicines-regulator-gives-approval....
-
- FDA, FDA takes key action in fight against COVID-19 by issuing emergency use authorization for first COVID-19 vaccine (2020); https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-takes-key-action....
-
- Haas E. J., Angulo F. J., McLaughlin J. M., Anis E., Singer S. R., Khan F., Brooks N., Smaja M., Mircus G., Pan K., Southern J., Swerdlow D. L., Jodar L., Levy Y., Alroy-Preis S., Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: An observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet 397, 1819–1829 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hall V. J., Foulkes S., Saei A., Andrews N., Oguti B., Charlett A., Wellington E., Stowe J., Gillson N., Atti A., Islam J., Karagiannis I., Munro K., Khawam J., Chand M. A., Brown C. S., Ramsay M., Lopez-Bernal J., Hopkins S.; SIREN Study Group , COVID-19 vaccine coverage in health-care workers in England and effectiveness of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against infection (SIREN): A prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet 397, 1725–1735 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

