Structural Basis of Pore Formation in the Mannose Phosphotransferase System by Pediocin PA-1
- PMID: 34851716
- PMCID: PMC8824269
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01992-21
Structural Basis of Pore Formation in the Mannose Phosphotransferase System by Pediocin PA-1
Abstract
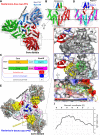
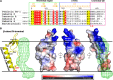
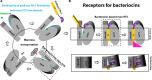
Bacteriocins are ribosomally synthesized bacterial antimicrobial peptides that have a narrow spectrum of antibacterial activity against species closely related to the producers. Pediocin-like (or class IIa) bacteriocins (PLBs) exhibit antibacterial activity against several Gram-positive bacterial strains by forming pores in the cytoplasmic membrane of target cells with a specific receptor, the mannose phosphotransferase system (man-PTS). In this study, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of man-PTS from Listeria monocytogenes alone and its complex with pediocin PA-1, the first and most extensively studied representative PLB, at resolutions of 3.12 and 2.45 Å, respectively. The structures revealed that the binding of pediocin PA-1 opens the Core domain of man-PTS away from its Vmotif domain, creating a pore through the cytoplasmic membranes of target cells. During this process, the N-terminal β-sheet region of pediocin PA-1 can specifically attach to the extracellular surface of the man-PTS Core domain, whereas the C-terminal half penetrates the membrane and cracks the man-PTS like a wedge. Thus, our findings shed light on a design of novel PLBs that can kill the target pathogenic bacteria. IMPORTANCE Listeria monocytogenes is a ubiquitous microorganism responsible for listeriosis, a rare but severe disease in humans, who become infected by ingesting contaminated food products (i.e., dairy, meat, fish, and vegetables): the disease has a fatality rate of 33%. Pediocin PA-1 is an important commercial additive used in food production to inhibit Listeria species. The mannose phosphotransferase system (man-PTS) is responsible for the sensitivity of Listeria monocytogenes to pediocin PA-1. In this study, we report the cryo-EM structures of man-PTS from Listeria monocytogenes alone and its complex with pediocin PA-1 at resolutions of 3.12 and 2.45 Å, respectively. Our results facilitate the understanding of the mode of action of class IIa bacteriocins as an alternative to antibiotics.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; antimicrobial peptides; bacteriocins; man-PTS; mannose phosphotransferase; pediocin PA-1; pediocin-like/class IIa bacteriocins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural Basis of the Immunity Mechanisms of Pediocin-like Bacteriocins.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jul 12;88(13):e0048122. doi: 10.1128/aem.00481-22. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35703550 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis of the Mechanisms of Action and Immunity of Lactococcin A, a Class IId Bacteriocin.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Mar 29;89(3):e0006623. doi: 10.1128/aem.00066-23. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36840592 Free PMC article.
-
Pediocin-Like Antimicrobial Peptides of Bacteria.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019 May;84(5):464-478. doi: 10.1134/S000629791905002X. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019. PMID: 31234762 Review.
-
High-level resistance to class IIa bacteriocins is associated with one general mechanism in Listeria monocytogenes.Microbiology (Reading). 2002 Aug;148(Pt 8):2361-2369. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-8-2361. Microbiology (Reading). 2002. PMID: 12177330
-
Pediocin-like bacteriocins: new perspectives on mechanism of action and immunity.Curr Genet. 2018 Apr;64(2):345-351. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0757-9. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28983718 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Bacteriocins and Bacteriocinogenic Beneficial Organisms in Food Products: Benefits, Challenges, Concerns.Foods. 2022 Oct 10;11(19):3145. doi: 10.3390/foods11193145. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for Biocontrol of Listeria monocytogenes Using Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Metabolites in Ready-to-Eat Meat- and Dairy-Ripened Products.Foods. 2022 Feb 14;11(4):542. doi: 10.3390/foods11040542. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35206018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum BPF2 and Pediococcus acidilactici ST6, Two Bacteriocinogenic Isolated Strains from Andalusian Spontaneous Fermented Sausages.Foods. 2023 Jun 21;12(13):2445. doi: 10.3390/foods12132445. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37444181 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Antimicrobials for Listeria monocytogenes in Ready-to-Eat Meats: Current Challenges and Future Prospects.Microorganisms. 2023 May 16;11(5):1301. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051301. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteriocins in Cancer Treatment: Mechanisms and Clinical Potentials.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 10;14(7):831. doi: 10.3390/biom14070831. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

