A Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia Revealing a Lepidic Adenocarcinoma: A Diagnostic Challenge during the Pandemic Period
- PMID: 34851783
- PMCID: PMC8887004
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202104-0826IM
A Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia Revealing a Lepidic Adenocarcinoma: A Diagnostic Challenge during the Pandemic Period
Figures
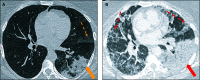

References
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol . 2011;6:244–285. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Venkata C, Mireles JA, Venkateshiah SB. Refractory hypoxemic respiratory failure due to adenocarcinoma of the lung with predominant bronchioloalveolar carcinoma component. Respir Care . 2009;54:1496–1499. - PubMed
-
- Wislez M, Massiani M-A, Milleron B, Souidi A, Carette M-F, Antoine M, et al. Clinical characteristics of pneumonic-type adenocarcinoma of the lung. Chest . 2003;123:1868–1877. - PubMed
-
- Trigaux JP, Gevenois PA, Goncette L, Gouat F, Schumaker A, Weynants P. Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: computed tomography findings. Eur Respir J . 1996;9:11–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

