CHK1 protects oncogenic KRAS-expressing cells from DNA damage and is a target for pancreatic cancer treatment
- PMID: 34852220
- PMCID: PMC8665414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110060
CHK1 protects oncogenic KRAS-expressing cells from DNA damage and is a target for pancreatic cancer treatment
Abstract
We apply genetic screens to delineate modulators of KRAS mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) sensitivity to ERK inhibitor treatment, and we identify components of the ATR-CHK1 DNA damage repair (DDR) pathway. Pharmacologic inhibition of CHK1 alone causes apoptotic growth suppression of both PDAC cell lines and organoids, which correlates with loss of MYC expression. CHK1 inhibition also activates ERK and AMPK and increases autophagy, providing a mechanistic basis for increased efficacy of concurrent CHK1 and ERK inhibition and/or autophagy inhibition with chloroquine. To assess how CHK1 inhibition-induced ERK activation promotes PDAC survival, we perform a CRISPR-Cas9 loss-of-function screen targeting direct/indirect ERK substrates and identify RIF1. A key component of non-homologous end joining repair, RIF1 suppression sensitizes PDAC cells to CHK1 inhibition-mediated apoptotic growth suppression. Furthermore, ERK inhibition alone decreases RIF1 expression and phenocopies RIF1 depletion. We conclude that concurrent DDR suppression enhances the efficacy of ERK and/or autophagy inhibitors in KRAS mutant PDAC.
Keywords: CHK1; DNA damage; ERK; KRAS; MYC; RIF1; pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.J.D. is a consultant/advisory board member for Anchiano Therapeutics, Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Mirati Therapeutics, and Revolution Medicines. C.J.D. has received research funding support from SpringWorks Therapeutics, Mirati Therapeutics, and Deciphera Pharmaceuticals and has consulted for Ribometrix, Sanofi, Jazz Therapeutics, Turning Point Therapeutics, and Eli Lilly. A.D.C. has consulted for Eli Lilly and Mirati Therapeutics. E.F.P. and M.P. receive royalties from Avant Diagnostics. E.F.P. is a consultant to and shareholder in Avant Diagnostics, Inc., and Perthera, Inc., and received funding support from Mirati Therapeutics, Genentech, Inc., and Abbvie, Inc.
Figures
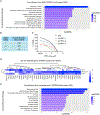
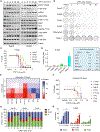




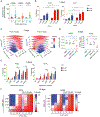
References
-
- Baldelli E, Calvert V, Hodge A, VanMeter A, Petricoin EF, and Pierobon M (2017). Reverse phase protein microarrays. In Molecular Profiling: Methods and Protocols, Espina V, ed. (New York: Springer; ), pp. 149–169. - PubMed
-
- Bennouna J, Lang I, Valladares-Ayerbes M, Boer K, Adenis A, Escudero P, Kim T-Y, Pover GM, Morris CD, and Douillard J-Y (2011). A phase II, open-label, randomised study to assess the efficacy and safety of the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) versus capecitabine monotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer who have failed one or two prior chemotherapeutic regimens. Invest. New Drugs 29, 1021–1028. - PubMed
-
- Bhowmick R, Thakur RS, Venegas AB, Liu Y, Nilsson J, Barisic M, and Hickson ID (2019). The RIF1-PP1 axis controls abscission timing in human cells. Curr. Biol 29, 1232–1242.e5. - PubMed
-
- Bodoky G, Timcheva C, Spigel DR, La Stella PJ, Ciuleanu TE, Pover G, and Tebbutt NC (2012). A phase II open-label randomized study to assess the efficacy and safety of selumetinib (AZD6244 [ARRY-142886]) versus capecitabine in patients with advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who have failed first-line gemcitabine therapy. Invest. New Drugs 30, 1216–1223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 CA221005/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009156/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA224081/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA199241/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA232529/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA175747/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA199235/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA239328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA251877/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA203657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA232113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA196510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA243253/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

