A case of improvement of clozapine-induced low leukocyte counts by adenine, cepharanthin and ninjin-yoei-to in a patient with treatment-resistant schizophrenia
- PMID: 34852834
- PMCID: PMC8638374
- DOI: 10.1186/s40780-021-00227-6
A case of improvement of clozapine-induced low leukocyte counts by adenine, cepharanthin and ninjin-yoei-to in a patient with treatment-resistant schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Although clozapine is the optimal drug for patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia, the drug has harmful adverse effects such as leukopenia. Adenine and cepharanthine are known to be effective for radiation- or drug-induced leukopenia. Furthermore, ninjin-yoei-to, a Chinese herbal medicine, augments the production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Thus, these drugs may be useful for clozapine-induced leukopenia.
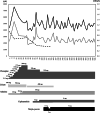
Case presentation: A 21 years-old woman with schizophrenia was hospitalized for initiation of clozapine treatment. Despite concomitant use of adenine, cepharanthine, and lithium carbonate having activities of increasing leukocytes, a decrease in leukocyte counts occurred after the initiation of clozapine. Additional administration of ninjin-yoei-to increased leukocyte counts, which prevented the development of leukopenia.
Conclusions: This is the first case that concomitant use of adenine, cepharanthin, and ninjin-yoei-to exhibited the effectiveness of reversing the decrease in leukocytes caused by clozapine. Monitoring leukocyte counts and preventing leukopenia are essential for successful treatment with clozapine for refractory schizophrenia. These medicines may be a potential option for preventing clozapine-induced leukopenia.
Keywords: Clozapine; Leukopenia; Ninjin-yoei-to; Treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ninjin-yoei-to (Ren-Shen-Yang-Rong-Tang) and Polygalae radix improves scopolamine-induced impairment of passive avoidance response in mice.Phytomedicine. 2003;10(6-7):467-73. doi: 10.1078/094471103322331403. Phytomedicine. 2003. PMID: 13678229
-
A traditional Chinese herbal medicine, ren-shen-yang-rong-tang (Japanese name: ninjin-yoei-to) augments the production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro.Int J Immunopharmacol. 1991;13(5):595-8. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(91)90081-h. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1991. PMID: 1723718
-
Changes of materials that scavenge 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radicals in plasma by per-oral administration of Kampo medicine, Ninjin-yoei-to in rats.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2003 Mar;55(3):367-71. doi: 10.1211/002235702711. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12724043
-
[Clozapine rechallenge after neutropenia in resistant schizophrenia: A review].Encephale. 2016 Aug;42(4):346-53. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Encephale. 2016. PMID: 27109327 Review. French.
-
Continuing clozapine treatment with lithium in schizophrenic patients with neutropenia or leukopenia: brief review of literature with case reports.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016 Feb;6(1):33-8. doi: 10.1177/2045125315624063. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26913176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Salomon JA, Vos T, Hogan DR, Gagnon M, Naghavi M, Mokdad A, Begum N, Shah R, Karyana M, Kosen S, Farje MR, Moncada G, Dutta A, Sazawal S, Dyer A, Seiler J, Aboyans V, Baker L, Baxter A, Benjamin EJ, Bhalla K, Abdulhak AB, Blyth F, Bourne R, Braithwaite T, Brooks P, Brugha TS, Bryan-Hancock C, Buchbinder R, Burney P, Calabria B, Chen H, Chugh SS, Cooley R, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahodwala N, Davis A, Degenhardt L, Díaz-Torné C, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Edmond K, Elbaz A, Ezzati M, Feigin V, Ferri CP, Flaxman AD, Flood L, Fransen M, Fuse K, Gabbe BJ, Gillum RF, Haagsma J, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Hel-Baqui A, Hoek HW, Hoffman H, Hogeland E, Hoy D, Jarvis D, Jonas JB, Karthikeyan G, Knowlton LM, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Lim SS, Lipshultz SE, Lopez AD, Lozano R, Lyons R, Malekzadeh R, Marcenes W, March L, Margolis DJ, McGill N, McGrath J, Mensah GA, Meyer AC, Michaud C, Moran A, Mori R, Murdoch ME, Naldi L, Newton CR, Norman R, Omer SB, Osborne R, Pearce N, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Pesudovs K, Phillips D, Pourmalek F, Prince M, Rehm JT, Remuzzi G, Richardson K, Room R, Saha S, Sampson U, Sanchez-Riera L, Segui-Gomez M, Shahraz S, Shibuya K, Singh D, Sliwa K, Smith E, Soerjomataram I, Steiner T, Stolk WA, Stovner LJ, Sudfeld C, Taylor HR, Tleyjeh IM, van der Werf MJ, Watson WL, Weatherall DJ, Weintraub R, Weisskopf MG, Whiteford H, Wilkinson JD, Woolf AD, Zheng ZJ, Murray CJL. Common values in assessing health outcomes from disease and injury: disability weights measurement study for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012;15(9859):2129–2143. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61680-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

