Body mass index is not associated with survival outcomes and immune-related adverse events in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma treated with the immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab
- PMID: 34852840
- PMCID: PMC8638339
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-021-03134-4
Body mass index is not associated with survival outcomes and immune-related adverse events in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma treated with the immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obese patients with solid tumors receiving anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)/PD-ligand-1(PD-L1) immune checkpoint inhibitors exhibit improved survival and higher risk of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) than those with a normal body mass index (BMI). In classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), the impact of BMI on survival and immune-related toxicity is unknown. We evaluated for the first time associations of BMI with survival and irAEs in patients with relapsed/refractory (RR)-cHL undergoing PD-1 blockade.
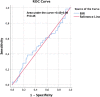
Methods: Data from a multicenter study on 133 patients treated with the anti-PD1 antibody nivolumab (July 2015-December 2016) were retrieved from a prospective database. Progression-free (PFS), overall survival (OS), incidence and severity of irAEs according to BMI categories were estimated by Kaplan-Meier method, landmark-analyses and Cox regressions.
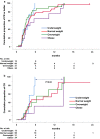
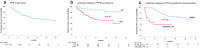
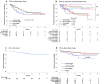
Results: Patients, mostly males (63%, n = 84) with a median age of 35 years (range, 15-82), advanced stage (75%), B symptoms (63%), bulky disease (24%), a median of 4 previous treatments (range, 1-9), received a median of 18 nivolumab doses (range, 1-57). No statistically significant differences across BMI subgroups emerged as to PFS, with 1-year rates of 67.1% for both normal weight (n = 66; 49.6%) and overweight (n = 31; 23.3%) patients. Underweight (n = 12; 9%) and obese (n = 24; 18%) patients had a 1-year PFS of 54.5% and 49%, respectively. In survival analyses, BMI either as a continuous (P = 0.5) or categorical (P for trend = 0.63) variable failed to associate with PFS. Response rates and time-to-response did not cluster in any BMI subset. No BMI-related differences in OS emerged across normal, overweight and obese patients but underweight patients had the worst survival. Occurrence of irAEs of whatever severity did not statistically associate with BMI.
Conclusions: In patients with RR-cHL receiving nivolumab, no statistically significant differences emerged in response rates, PFS and OS across BMI categories of normal weight, overweight and obese. Overweight/obese patients did not display an increased risk of irAEs. The exquisite sensitivity to anti-PD-1 antibodies, the unique cytokine milieu and effector pathways triggered by nivolumab in cHL, may represent biologic 'equalizers' counteracting the immunoregulatory effects of adiposity. Differently from solid tumors, BMI is not associated with treatment efficacy and immune-related toxicity and does not represent a predictive tool for PD-1-targeted immunotherapies in cHL.
Keywords: Body mass index; Hodgkin lymphoma; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immune-related adverse events.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Rosaria De Filippi has shared patent applications with EDO-Mundipharma irrelevant to the present research. Armando Santoro declares honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Servier, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Eisai, Bayer, MSD, Takeda, Roche, Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Arqule, Lilly, Sandoz, and Novartis; all irrelevant to the present research. Luigi Rigacci declares honoraria from Merck Sharp & Dohme and Bristol-Myers Squibb; all irrelevant to the present research. Pier Luigi Zinzani declares honoraria from Verastem, Celltrion, Gilead, Janssen-Cilag, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Servier, Sandoz, MERCK Sharp & Dohme, TG Thera, Takeda, Roche, Eusapharma, Kyowa-Kirin, Novartis, ADC-Therapeutics, Incyte, Beigene; all irrelevant to the present research. Antonio Pinto declares honoraria from BRISTOL-Myers Squibb, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Helssin Healthcare, Janssen, Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Incyte, Servier, Merck Sharp & Dohme and Takeda; all irrelevant to the present research. All the other authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Another side of the association between body mass index (BMI) and clinical outcomes of cancer patients receiving programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)/ Programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) checkpoint inhibitors: A multicentre analysis of immune-related adverse events.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Mar;128:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.12.031. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32109847
-
Outcomes and Toxicities of Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) Inhibitors in Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients in the United States: A Real-World, Multicenter Retrospective Analysis.Oncologist. 2019 Jul;24(7):955-962. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0538. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30568021 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Body Mass Index With the Safety Profile of Nivolumab With or Without Ipilimumab.JAMA Oncol. 2023 Jan 1;9(1):102-111. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.5409. JAMA Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36480191 Free PMC article.
-
[Checkpoint inhibitors in Hodgkin lymphoma].Internist (Berl). 2020 Jul;61(7):660-668. doi: 10.1007/s00108-020-00811-2. Internist (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32462248 Review. German.
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Dendritic Cell Cancer Vaccination: The Synergy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Combined Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7509. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147509. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Plasma Proteins as Biomarkers for Immunotherapy Toxicity: Insights from Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 14;13(7):1717. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071717. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722787 Free PMC article.
-
CD39 and LDHA affects the prognostic role of NLR in metastatic melanoma patients treated with immunotherapy.J Transl Med. 2023 Sep 8;21(1):610. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04419-6. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37684649 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Factors of Response to Immunotherapy in Lymphomas: A Multicentre Clinical Data Warehouse Study (PRONOSTIM).Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 9;15(16):4028. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164028. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627056 Free PMC article.
-
Body mass index-associated responses to an ABVD-like regimen in newly-diagnosed patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 23;14:1195907. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1195907. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37680722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cortellini A, Bersanelli M, Santini D, et al. Another side of the association between body mass index (BMI) and clinical outcomes of cancer patients receiving programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)/ Programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) checkpoint inhibitors: a multicentre analysis of immune-related adverse events. Eur J Cancer. 2020;128:17–26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.12.031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

