GP73 is a TBC-domain Rab GTPase-activating protein contributing to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without obesity
- PMID: 34853313
- PMCID: PMC8636488
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27309-1
GP73 is a TBC-domain Rab GTPase-activating protein contributing to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without obesity
Abstract
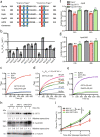
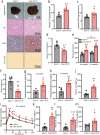
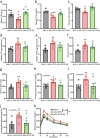
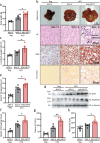
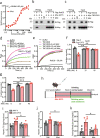
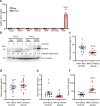
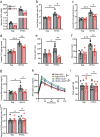
The prevalence of non-obese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasing worldwide with unclear etiology and pathogenesis. Here, we show GP73, a Golgi protein upregulated in livers from patients with a variety of liver diseases, exhibits Rab GTPase-activating protein (GAP) activity regulating ApoB export. Upon regular-diet feeding, liver-GP73-high mice display non-obese NAFLD phenotype, characterized by reduced body weight, intrahepatic lipid accumulation, and gradual insulin resistance development, none of which can be recapitulated in liver-GAP inactive GP73-high mice. Common and specific gene expression signatures associated with GP73-induced non-obese NAFLD and high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese NAFLD are revealed. Notably, metformin inactivates the GAP activity of GP73 and alleviates GP73-induced non-obese NAFLD. GP73 is pathologically elevated in NAFLD individuals without obesity, and GP73 blockade improves whole-body metabolism in non-obese NAFLD mouse model. These findings reveal a pathophysiological role of GP73 in triggering non-obese NAFLD and may offer an opportunity for clinical intervention.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lack of ClC-2 Alleviates High Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(6):2187-2198. doi: 10.1159/000488164. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29550812
-
Hepatic STAMP2 alleviates high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance.J Hepatol. 2015 Aug;63(2):477-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.01.025. Epub 2015 Jan 31. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25646886
-
Depletion of B cell-activating factor attenuates hepatic fat accumulation in a murine model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 30;9(1):977. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37403-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30700810 Free PMC article.
-
Rescue of Hepatic Phospholipid Remodeling Defectin iPLA2β-Null Mice Attenuates Obese but Not Non-Obese Fatty Liver.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 17;10(9):1332. doi: 10.3390/biom10091332. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32957701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
It Is High Time Physicians Thought of Natural Products for Alleviating NAFLD. Is There Sufficient Evidence to Use Them?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 14;22(24):13424. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413424. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Golgi Protein 73 (GP73) for Liver Fibrosis Staging in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Scoping Review and Cohort Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 24;15(5):544. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050544. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075792 Free PMC article.
-
VLDL Biogenesis and Secretion: It Takes a Village.Circ Res. 2024 Jan 19;134(2):226-244. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323284. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Circ Res. 2024. PMID: 38236950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GP73 reinforces cytotoxic T-cell function by regulating HIF-1α and increasing antitumor efficacy.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jan 6;13(1):e009265. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009265. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39762082 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, and Predictors of Nonobese Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Nov 25;17:4397-4406. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S482638. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39619223 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi protein 73: the driver of inflammation in the immune and tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 8;15:1508034. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1508034. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39845976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buzzetti E, Pinzani M, Tsochatzis EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Metabolism. 2016;65:1038–1048. - PubMed
-
- Brunt EM, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015;1:15080. - PubMed
-
- Eslam M, Fan JG, Mendez-Sanchez N. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-obese individuals: the impact of metabolic health. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020;5:713–715. - PubMed
-
- Ye Q, et al. Global prevalence, incidence, and outcomes of non-obese or lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020;5:739–752. - PubMed
-
- Kim D, Kim WR. Nonobese fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;15:474–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

