The computational analyses, molecular dynamics of fatty-acid transport mechanism to the CD36 receptor
- PMID: 34853341
- PMCID: PMC8636502
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-01373-5
The computational analyses, molecular dynamics of fatty-acid transport mechanism to the CD36 receptor
Abstract
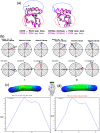
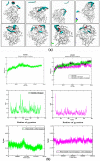
The transmembrane glycoprotein CD36, which is responsible of the metabolic disorders, and the elevated intake of fat induces lipid buildup, is a multifunctional scavenger receptor signaling those functions in high-affinity tissue uptake of long-chain fatty acids. In this study, we used series of molecular dynamics simulations of the wild type and mutants types K164A CD36 protein interacting with one palmitic acid (PLM) besides simulations of the wild type interacting with the three PLM to find out the mechanism of the functioning of the complex CD36/Fatty acids and the unraveling of the role of the mutation. Additionally we determined whether Lys164, mostly exposed to protein surface, played important roles in fatty acid uptake. These simulations revealed, the conformational changes induced by Lys164 residue and the altered interactions induced by the mutagenesis of surface lysine that was badly influencing the folding, utility, solubility, and stability form of the variant. Furthermore, Lys164 residue provided the structural basis of forming an opening at the region of principal portal for the dissociation of palmitic acid. The results of our simulations revealed hole two fatty acids found in CD36 cavity structure and it was the most preferred to CD36 structure stabilization.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dynamic role of the transmembrane glycoprotein CD36 (SR-B2) in cellular fatty acid uptake and utilization.J Lipid Res. 2018 Jul;59(7):1084-1093. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R082933. Epub 2018 Apr 7. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29627764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of CD36 in Palmitic Acid Lipotoxicity in Neuro-2a Neuroblastoma Cells.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 22;11(11):1567. doi: 10.3390/biom11111567. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827565 Free PMC article.
-
A novel function for fatty acid translocase (FAT)/CD36: involvement in long chain fatty acid transfer into the mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2004 Aug 27;279(35):36235-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400566200. Epub 2004 May 25. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15161924
-
Critical residues and motifs for homodimerization of the first transmembrane domain of the plasma membrane glycoprotein CD36.J Biol Chem. 2017 May 26;292(21):8683-8693. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.779595. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28336533 Free PMC article.
-
The enigmatic membrane fatty acid transporter CD36: New insights into fatty acid binding and their effects on uptake of oxidized LDL.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018 Nov;138:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 20. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018. PMID: 27288302 Review.
Cited by
-
Intermolecular Mechanism and Dynamic Investigation of Avian Influenza H7N9 Virus' Susceptibility to E119V-Substituted Peramivir-Neuraminidase Complex.Molecules. 2022 Mar 2;27(5):1640. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051640. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268741 Free PMC article.
-
Large scale peptide screening against main protease of SARS CoV-2.J Comput Chem. 2023 Mar 30;44(8):887-901. doi: 10.1002/jcc.27050. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Comput Chem. 2023. PMID: 36478400 Free PMC article.
-
The association of soluble cluster of differentiation 36 with metabolic diseases: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target.Pediatr Discov. 2023 Jun 12;1(1):e9. doi: 10.1002/pdi3.9. eCollection 2023 Jun. Pediatr Discov. 2023. PMID: 40625574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human CD36: Gene Regulation, Protein Function, and Its Role in Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;16(6):705. doi: 10.3390/genes16060705. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

