Losartan improves intestinal mucositis induced by 5-fluorouracil in mice
- PMID: 34853351
- PMCID: PMC8636633
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-01969-x
Losartan improves intestinal mucositis induced by 5-fluorouracil in mice
Abstract
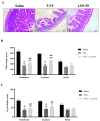
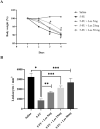
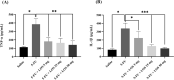
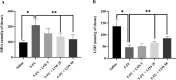
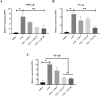
Intestinal mucositis (IM) is a common side effect of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-based chemotherapy, which negatively impacts therapeutic outcomes and delays subsequent cycles of chemotherapy resulting in dose reductions and treatment discontinuation. In search of new pharmacological alternatives that minimize your symptoms, this work set out to study the effect of losartan (LOS), a receptor type I (AT1) angiotensin II antagonist, on intestinal mucositis induced by 5-FU. Intestinal mucositis was induced by a single intraperitoneal administration of 5-FU (450 mg/kg) in Swiss mice. Losartan (5, 25 or 50 mg/kg) or saline was orally administered 30 min before 5-FU and daily for 4 days. On 4th day, the animals were euthanized and segments of small intestine were collected to evaluate histopathological alterations (morphometric analysis), concentration of inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress markers and genic expression of NF-κB p65, Fn-14 and TWEAK. Weight evaluation and changes in leukogram were also analyzed. 5-FU induced intense weight loss, leukopenia and reduction in villus height compared to saline group. Losartan (50 mg/kg) prevented 5-FU-induced inflammation by decreasing in the analyzed parameters compared to the 5-FU group. Our findings suggest that 50 mg/kg of losartan prevents the effects of 5-FU on intestinal mucosa in mice.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduced apoptosis and attenuated intestinal mucositis in a 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy model in mice.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Jul;68(1):87-96. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1451-5. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20844880
-
Diadzein ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in rodents.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 15;843:292-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.12.014. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30529194
-
Alanyl-glutamine attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015 Jun;48(6):493-501. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20144360. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 25945744 Free PMC article.
-
Irinotecan- and 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis: insights into pathogenesis and therapeutic perspectives.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;78(5):881-893. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3139-y. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27590709 Review.
-
Possible cytoprotective mechanisms of oxytocin against 5-fluorouracil-induced gastrointestinal mucositis.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 May;49(5):4055-4059. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07384-3. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35474056 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential of Glycyrrhiza from "Medicine Food Homology" in the Fight against Digestive System Tumors.Molecules. 2023 Nov 22;28(23):7719. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237719. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental Chemotherapy-Induced Mucositis: A Scoping Review Guiding the Design of Suitable Preclinical Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 6;23(23):15434. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315434. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499758 Free PMC article.
-
Verbascoside restores gastrointestinal integrity and attenuates inflammation in a rat model of 5-FU-induced mucositis.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 16;42(7):267. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02823-0. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40524059 Free PMC article.
-
Binding mechanism and SERS spectra of 5-fluorouracil on gold clusters.Front Chem. 2022 Dec 5;10:1050423. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1050423. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36545217 Free PMC article.
-
The traditional knowledge about the biodiversity of edible Brazilian fruits and their pollinators: an integrative review.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025 Mar 3;21(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13002-025-00769-1. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025. PMID: 40033295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen H, Zhang F, Li R, Liu Y, Wang X, Zhang X, et al. Berberine regulates fecal metabolites to ameliorate 5-fluorouracil induced intestinal mucositis through modulating gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020;124:109829. - PubMed
-
- Arends J. How to feed patients with gastrointestinal mucositis. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care. 2018;12(2):168–173. - PubMed
-
- Sonis ST. The pathobiology of mucositis. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004;4(4):277–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

