A comprehensive in silico investigation into the nsSNPs of Drd2 gene predicts significant functional consequences in dopamine signaling and pharmacotherapy
- PMID: 34853389
- PMCID: PMC8636637
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-02715-z
A comprehensive in silico investigation into the nsSNPs of Drd2 gene predicts significant functional consequences in dopamine signaling and pharmacotherapy
Abstract
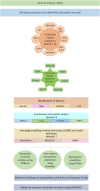
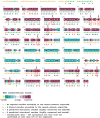
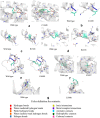
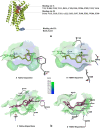
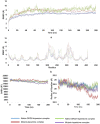
DRD2 is a neuronal cell surface protein involved in brain development and function. Variations in the Drd2 gene have clinical significance since DRD2 is a pharmacotherapeutic target for treating psychiatric disorders like ADHD and schizophrenia. Despite numerous studies on the disease association of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the intronic regions, investigation into the coding regions is surprisingly limited. In this study, we aimed at identifying potential functionally and pharmaco-therapeutically deleterious non-synonymous SNPs of Drd2. A wide array of bioinformatics tools was used to evaluate the impact of nsSNPs on protein structure and functionality. Out of 260 nsSNPs retrieved from the dbSNP database, initially 9 were predicted as deleterious by 15 tools. Upon further assessment of their domain association, conservation profile, homology models and inter-atomic interaction, the mutant F389V was considered as the most impactful. In-depth analysis of F389V through Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation revealed a decline in affinity for its native agonist dopamine and an increase in affinity for the antipsychotic drug risperidone. Remarkable alterations in binding interactions and stability of the protein-ligand complex in simulated physiological conditions were also noted. These findings will improve our understanding of the consequence of nsSNPs in disease-susceptibility and therapeutic efficacy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigating the structural impact of S311C mutation in DRD2 receptor by molecular dynamics & docking studies.Biochimie. 2016 Apr;123:52-64. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26805384
-
Comprehensive Characterization of the Coding and Non-Coding Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Tumor Protein p63 (TP63) Gene Using In Silico Tools.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 20;11(11):1733. doi: 10.3390/biom11111733. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827731 Free PMC article.
-
Extrapolating the effect of deleterious nsSNPs in the binding adaptability of flavopiridol with CDK7 protein: a molecular dynamics approach.Hum Genomics. 2013 Apr 5;7(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-7-10. Hum Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23561625 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenetics of D2 dopamine receptor gene in prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010 Jan;6(1):43-53. doi: 10.1517/17425250903352501. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 19929252 Review.
-
Association between dopamine receptor gene polymorphisms and effects of risperidone treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Jan;124(1):94-104. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13111. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30103286
Cited by
-
Dopamine D2 receptor gene Taq 1A polymorphism: genetic architecture in Indian population and comparison to global populations.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 14;16:1610364. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1610364. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40727586 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of pathogenic germline variants in gastric cancer and development of "GasCanBase" database.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Dec;6(12):e1906. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1906. Epub 2023 Oct 22. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 37867380 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of highly deleterious non-synonymous polymorphisms on GRIN2A protein's structure and function.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 15;18(6):e0286917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286917. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37319252 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural analysis of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in the MYB oncoproteins associated with human cancer.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 17;11(1):24206. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03624-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34921182 Free PMC article.
-
The World of GPCR dimers - Mapping dopamine receptor D2 homodimers in different activation states and configuration arrangements.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Sep 3;21:4336-4353. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.08.032. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37711187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hacia JG, et al. Determination of ancestral alleles for human single-nucleotide polymorphisms using high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Genet. 1999;22:164–167. - PubMed
-
- Cargill M, et al. Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes. Nat. Genet. 1999;22:231–238. - PubMed
-
- Lee JE, Choi JH, Lee JH, Lee MG. Gene SNPs and mutations in clinical genetic testing: Haplotype-based testing and analysis. Mutat. Res. 2005;573:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Collins FS, Brooks LD, Chakravarti A. A DNA polymorphism discovery resource for research on human genetic variation. Genome Res. 1998;8:1229–1231. - PubMed
-
- Alexander RP, Fang G, Rozowsky J, Snyder M, Gerstein MB. Annotating non-coding regions of the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010;11:559–571. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

