SETD5 modulates homeostasis of hematopoietic stem cells by mediating RNA Polymerase II pausing in cooperation with HCF-1
- PMID: 34853439
- PMCID: PMC8979820
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-021-01481-1
SETD5 modulates homeostasis of hematopoietic stem cells by mediating RNA Polymerase II pausing in cooperation with HCF-1
Abstract
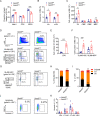
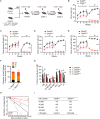
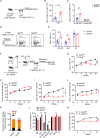
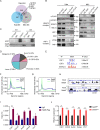
SETD5 mutations were identified as the genetic causes of neurodevelopmental disorders. While the whole-body knockout of Setd5 in mice leads to embryonic lethality, the role of SETD5 in adult stem cell remains unexplored. Here, a critical role of Setd5 in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) is identified. Specific deletion of Setd5 in hematopoietic system significantly increased the number of immunophenotypic HSCs by promoting HSC proliferation. Setd5-deficient HSCs exhibited impaired long-term self-renewal capacity and multiple-lineage differentiation potentials under transplantation pressure. Transcriptome analysis of Setd5-deficient HSCs revealed a disruption of quiescence state of long-term HSCs, a cause of the exhaustion of functional HSCs. Mechanistically, SETD5 was shown to regulate HSC quiescence by mediating the release of promoter-proximal paused RNA polymerase II (Pol II) on E2F targets in cooperation with HCF-1 and PAF1 complex. Taken together, these findings reveal an essential role of SETD5 in regulating Pol II pausing-mediated maintenance of adult stem cells.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Schuettengruber B, Martinez AM, Iovino N, Cavalli G. Trithorax group proteins: switching genes on and keeping them active. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:799–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

