Dose-Related Inhibition of Capsaicin Responses by Cannabinoids CBG, CBD, THC and their Combination in Cultured Sensory Neurons
- PMID: 34853533
- PMCID: PMC8627890
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S336773
Dose-Related Inhibition of Capsaicin Responses by Cannabinoids CBG, CBD, THC and their Combination in Cultured Sensory Neurons
Abstract
Background: The analgesic effects of Cannabis sativa are mediated by ∆9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), but the contributions of other bioactive complex components, including cannabigerol (CBG) and cannabidiol (CBD), are unclear. We describe the individual and combined effects of CBG, CBD and THC, on blocking capsaicin responses in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, in an in vitro model of nociceptor hypersensitivity.
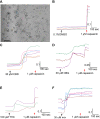
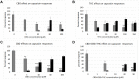
Materials and methods: Adult rat DRG were dissected and enzyme digested to obtain a neuronal suspension in BSF2 medium containing 2% fetal calf serum, and the neurotrophic factors NGF and GDNF. After 48 h, cultured neurons were loaded with Fura-2 AM, to determine the effects of cannabinoids on capsaicin responses using calcium imaging. In control experiments, neurons were treated with vehicle, followed by 1 µM capsaicin. In cannabinoid treated cultures, CBG, CBD or THC were applied individually, or combined (1:1:1 ratio), followed by 1 µM capsaicin. Data from n = 6 experiments were analysed with Student's t-test and Pearson's correlation coefficient.
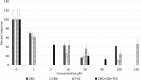
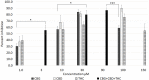
Results: CBG, CBD and THC, applied individually, elicited dose-related calcium influx in a subset of DRG neurons, and a corresponding dose-related reduction of subsequent responses to capsaicin. Maximum inhibition of capsaicin responses was observed at 30 µM CBG, 100 µM CBD, and 100 µM THC individually, and with combined CBD+CBG+THC (1:1:1) at 90 µM. THC+CBD+CBG combined in a 1:1:1 proportion has the potential to enhance the potency of these compounds applied individually. There was a high correlation between cannabinoid-mediated calcium influx and reduction of capsaicin responses: CBG = -0.88, THC = -0.97, CBD = -0.99 and combined CBG + THC + CBD = -1.00.
Conclusion: CBG, CBD and THC demonstrated potent dose-related inhibition of capsaicin responses in DRG neurons when applied individually in vitro, and enhanced when applied in combination, being most effective at 90 μM. Thus, efficacy and tolerability of THC could be improved in combination with CBG and CBD at optimal concentrations, which deserve further studies in vivo.
Keywords: CBD; CBG; DRG neurons; THC; TRPV1; cannabinoid; pain.
© 2021 Anand et al.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by EMMAC Life Sciences Ltd. Barbara Pacchetti and Mikael H Sodergren are employees of EMMAC Life Sciences Ltd. Barbara Pacchetti reports personal fees from EMMAC Life Sciences, outside the submitted work. Mikael H Sodergren reports consultancy for and personal fees from Emmac Life Sciences, outside the submitted work. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed and report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Merskey H, Bogduk N, editors, IASP Task Force on Taxonomy, Part III: Pain Terms, a Current List with Definitions and Notes on Usage. Seattle, WA: IASP Press; 1994:209–214.
-
- Anand U. Mechanisms and management of cancer pain. Alison E, editor. The Cancer Handbook; Copyright © 2005 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Chapter 310; 2005.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

