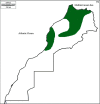
An Insight into Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Nutritional Properties of Arbutus unedo L. from Morocco
- PMID: 34853597
- PMCID: PMC8629616
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1794621
An Insight into Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Nutritional Properties of Arbutus unedo L. from Morocco
Abstract
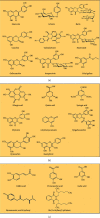
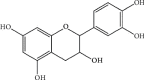
Arbutus unedo L. (Ericaceae) is an evergreen shrub widely distributed in the Mediterranean region, particularly through the Moroccan forests. It is an important medicinal plant of great scientific interest due to its nutritional, pharmacological, and chemical properties. The objective of this review is to provide insights into traditional medicinal uses and phytochemical and pharmacological properties of A. unedo from Morocco. In Morocco, the plant has been used as a traditional medicine to treat several pathological conditions. Many phytochemical compounds have been reported in the plant, of which vitamins, carotenoids, flavonoids, polyphenols, tannins, and their derivatives are the most prevalent. Leaves and fruits of A. unedo contain the most significant number of phytochemicals among the species. Furthermore, researchers have demonstrated that A. unedo exhibited antioxidant, anticancer, antibacterial, antidiabetic, antiaggregant, and antihypertensive activities due to the presence of many biochemical compounds with health-promoting properties. According to different toxicity tests, the use of A. unedo is devoid of any significant side effects and/or toxicity. Despite its nutraceutical and health-promoting properties, Moroccan A. unedo remains underexploited mainly, and most of its traditional uses have not yet undergone scientific evidence-based research; therefore, improved knowledge about the potential value of the plant would allow understanding of its biological activity based on its phytochemical compounds that may contribute to the species preservation and valorization.
Copyright © 2021 Mohammed El Haouari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- El Haouari M., Rosado J. A. Phytochemical, anti-diabetic and cardiovascular properties of urtica dioica L. (urticaceae): a review. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry . 2019;19(1):63–71. - PubMed
-
- WHO. WHO Guidelines on Safety Monitoring of Herbal Medicines in Pharmacovigilance Systems . Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- WHO. Regulatory Situation of Herbal Medicines: A Worldwide Review . Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization (WHO); 1998.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

