Jinwujiangu Capsule Treats Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis via the NLRP3/CAPSES/GSDMD Pathway
- PMID: 34853599
- PMCID: PMC8629621
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/4836992
Jinwujiangu Capsule Treats Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting Pyroptosis via the NLRP3/CAPSES/GSDMD Pathway
Abstract
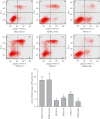
Jinwujiangu capsule (JWJGC) is a traditional Chinese medicine formula used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, whether its mechanism is associated with pyroptosis remains unclear. In this study, the ability of JWJGC to inhibit the growth of fibroblast-like synoviocytes of RA (RA-FLS) through pyroptosis was evaluated. The cells isolated from patients with RA were identified by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. After RA-FLS were treated with different concentrations of JWJGC-containing serum, the cell proliferation inhibition rate, expression of caspase-1/3/4/5, NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), gasdermin-D (GSDMD), and apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), concentrations of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18), the activity of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), and pyroptosis were evaluated. The results showed that JWJGC increased the proliferative inhibition rate, decreased the expression of caspase-1/3/4/5, GSDMD, NLRP3, and ASC, suppressed the expression of IL-1β and IL-18, induced the activity of LDH, and downregulated the number of double-positive FITC anti-caspase-1 and PI. Generally, our findings suggest that JWJGC can regulate NLRP3/CAPSES/GSDMD in treating RA-FLS through pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2021 Yi Ling et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SMAD2 inhibits pyroptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and secretion of inflammatory factors via the TGF-β pathway in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Aug 9;25(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03136-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37559090 Free PMC article.
-
[Huangdi Anxiao Capsules-containing serum protects cell model from cognitive dysfunction in diabetes via inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Oct;48(19):5315-5325. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230614.702. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38114121 Chinese.
-
Periplogenin inhibits pyroptosis of fibroblastic synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis through the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 May 30;133:112041. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112041. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38636373
-
[Effects of serum from Xinfeng capsule-treated rats on lipopolysaccharide-induced pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Dec 20;42(12):1846-1851. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.12.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36651253 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Gasdermin D in pyroptosis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Sep;11(9):2768-2782. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34589396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic and therapeutic insights into the function of NLRP3 inflammasome in sterile arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 25;14:1273174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273174. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37954594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can pyroptosis be a new target in rheumatoid arthritis treatment?Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 22;14:1155606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155606. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37426634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol alleviates rheumatoid arthritis through pyroptosis based on bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 30;14(1):29769. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81833-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39616227 Free PMC article.
-
New Potentiality of Bioactive Substances: Regulating the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Autoimmune Diseases.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 28;15(21):4584. doi: 10.3390/nu15214584. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic and therapeutic insights into the function of different cell death modalities in rheumatoid arthritis: emphasis on the crosstalk with non-coding RNAs.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 23;16:1620209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1620209. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40771812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

