A Novel Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature to Predict Prognosis in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 34853622
- PMCID: PMC8629675
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5759927
A Novel Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature to Predict Prognosis in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
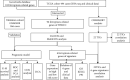
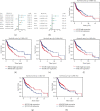
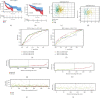
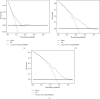
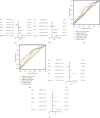
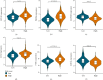
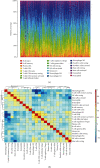
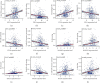
The clinical TNM staging system is currently used to evaluate the prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). The 5-year survival rate for patients with HNSCC is less than 50%, which is attributed to the lack of reliable prognostic biomarkers. Ferroptosis-related genes (FRGs) regulate cancer initiation and progression. Therefore, we analyzed the correlation between FRGs and the clinical outcomes of patients with HNSCC. A typical prognostic model of FRGs for HNSCC was constructed using bioinformatics tools and data from public databases, including The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and GeneCards. The model was generated based on the following six FRGs: ATG5, PRDX6, OTUB1, FTH1, SOCS1, and MAP3K5. The accuracy of model prediction was analyzed systematically. The overall survival (OS) of the high-risk group was significantly lower than that of the low-risk group. The AUC for 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival were 0.645, 0.721, and 0.737, respectively, in the training set (TCGA cohort) and 0.726, 0.620, and 0.584, respectively, in the validation set (GSE65858). The multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that the risk score was an independent prognostic factor for HNSCC. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses revealed that six FRGs were enriched in the ferroptosis pathway. A novel FRG prognostic signature model was established for HNSCC. The findings of this study reveal that FRGs are potential biomarkers for HNSCC.
Copyright © 2021 Li Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a novel ferroptosis-related gene signature for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Sep;98:107789. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107789. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34130150
-
Development and validation of a fourteen- innate immunity-related gene pairs signature for predicting prognosis head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2020 Oct 20;20(1):1015. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07489-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33081731 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of an individualized prognostic signature of lung squamous cell carcinoma based on ferroptosis-related genes.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Dec;12(23):3236-3247. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14195. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34672420 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review regarding the association of E2Fs with the prognosis and immune infiltrates in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Asian J Surg. 2024 May;47(5):2106-2121. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2024.01.130. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Asian J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38320907 Review.
-
Advances in the study of regulators of ferroptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Jun;51(6):45. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5248. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37052257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signatures: Prognostic Role in HPV-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 5;17(3):530. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030530. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941896 Free PMC article.
-
CD46 TREM1 regulates the autophagy marker LC3B ATG5 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 May 22;15:1579282. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1579282. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40475017 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxiredoxin 6 in Stress Orchestration and Disease Interplay.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 23;14(4):379. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040379. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Deubiquitinating Enzyme in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):552. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010552. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SENP1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating ACSL4 protein stability via SUMO1.Oncol Rep. 2024 Feb;51(2):34. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8693. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38186303 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

