The roles and mechanisms of the m6A reader protein YTHDF1 in tumor biology and human diseases
- PMID: 34853726
- PMCID: PMC8609105
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.023
The roles and mechanisms of the m6A reader protein YTHDF1 in tumor biology and human diseases
Abstract
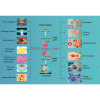
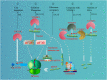
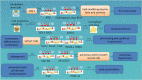
YTHDF1 is the most versatile and powerful reader protein of N 6-methyladenosine (m6A)-modified RNA, and it can recognize both G(m6A)C and A(m6A)C RNAs as ligands without sequence selectivity. YTHDF1 regulates target gene expression by different mechanisms, such as promoting translation or regulating the stability of mRNA. Numerous studies have shown that YTHDF1 plays an important role in tumor biology and nontumor lesions by mediating the protein translation of important genes or by affecting the expression of key factors involved in many important cell signaling pathways. Therefore, in this review we focus on some of the roles of YTHDF1 in tumor biology and diseases.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; YTHDF1; m6A; mRNA stability; protein translation; tumor biology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sevoflurane impairs m6A-mediated mRNA translation and leads to fine motor and cognitive deficits.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022 Apr;38(2):347-369. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09601-4. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 33928466
-
The m6A reader YTHDF1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via augmenting EIF3C translation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 17;48(7):3816-3831. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa048. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31996915 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA m6A Reader YTHDF1 Is Required for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Progression.Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 15;83(6):845-860. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-4249. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36634204
-
N6-Methyladenosine RNA-Binding Protein YTHDF1 in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Function, Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Implication.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;14(14):3489. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143489. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jan 28;9(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01321-4. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36707507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-canonical translation in cancer: significance and therapeutic potential of non-canonical ORFs, m6A-modification, and circular RNAs.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Sep 27;10(1):412. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02185-y. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39333489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YTHDF1 promotes gallbladder cancer progression via post-transcriptional regulation of the m6A/UHRF1 axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(9):e18328. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18328. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38683130 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 as a master regulator of translation in cancer: mechanisms and implications.NAR Cancer. 2024 Mar 5;6(1):zcae009. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae009. eCollection 2024 Mar. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38444581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3-dependent m6A modification of PSEN1 mRNA regulates craniofacial development through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Mar 20;15(3):229. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06606-9. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38509077 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and mechanisms of RNA m6A regulators in breast cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Sep;65(3):86. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5674. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39054967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang J., Wang K., Liu W., Cai Y., Jin H. m6A mRNA methylation regulates the development of gestational diabetes mellitus in Han Chinese women. Genomics. 2021;113:1048–1056. - PubMed
-
- Qin Y., Qiao Y., Li L., Luo E., Wang D., Yao Y., Tang C., Yan G. The mA methyltransferase METTL3 promotes hypoxic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Life Sci. 2021;274:119366. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources