Long-Term Carbohydrate-Containing Late-Evening Snack Significantly Improves the Ratio of Branched Chain Amino Acids to Aromatic Amino Acids in Adults with Liver Cirrhosis due to Hepatitis B
- PMID: 34853787
- PMCID: PMC8629637
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1074565
Long-Term Carbohydrate-Containing Late-Evening Snack Significantly Improves the Ratio of Branched Chain Amino Acids to Aromatic Amino Acids in Adults with Liver Cirrhosis due to Hepatitis B
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Long-Term Carbohydrate-Containing Late-Evening Snack Significantly Improves the Ratio of Branched Chain Amino Acids to Aromatic Amino Acids in Adults with Liver Cirrhosis due to Hepatitis B.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9821414. doi: 10.1155/2024/9821414. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38550013 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The liver is the primary organ for amino acid metabolism, and metabolic disorder of amino acids is common in liver disease. However, the characteristics of plasma amino acid profiles in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis and the impacts of late-evening snack (LES) on cirrhosis are unclear.
Objectives: To investigate the characteristics of plasma amino acid profiles in patients with HBV-related chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and the effects of late-evening snacks on plasma amino acid profiles.
Methods: 86 patients with HBV-related cirrhosis and eighty patients with chronic hepatitis B were included in this study. The plasma amino acid profiles were measured by the amino acid analyzer. Patients were randomly divided into two groups, of which the liver cirrhosis group was to receive daily LES (n = 43) or non-LES (n = 43) for 6 months. Plasma amino acid profiles and biochemical parameters were measured in both groups at baseline and after 1, 3, and 6 months.
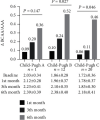
Results: Compared to healthy controls, the plasma concentration in the liver cirrhosis group of threonine, serine, glycine, glutamine, cysteine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, arginine, and methionine increased significantly (P < 0.05), while the ratio of branched chain amino acids (BCAA) to aromatic amino acids (AAA) decreased significantly (P < 0.05). A carbohydrate-predominant LES treatment resulted in a significant increase in BCAA/AAA and decrease in the level of ammonia and glutamine compared with baseline after 6 months of supplementation (P < 0.05). Patients with Child-Pugh B and C are more responsive to changes in amino acid profiles than those with Child-Pugh A.
Conclusions: The application of an LES carbohydrate module for six months in liver cirrhosis patients was associated with increased BCAA/AAA and decreased level of ammonia. Patients with Child-Pugh B and C grades were the most beneficial population.
Copyright © 2021 Wei Hou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Late evening snacks with branched-chain amino acids improve the Fischer ratio with patients liver cirrhosis at fasting in the next morning.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2019 Apr;30:138-144. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2019.01.003. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2019. PMID: 30904214
-
Role of meal carbohydrate content for the imbalance of plasma amino acids in patients with liver cirrhosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Aug;22(8):1241-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04620.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17688664 Clinical Trial.
-
Ammonia and amino acid profiles in liver cirrhosis: effects of variables leading to hepatic encephalopathy.Nutrition. 2015 Jan;31(1):14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.03.016. Epub 2014 Mar 30. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 25220875 Review.
-
Effect of long-term oral supplementation with branched-chain amino acid granules on the prognosis of liver cirrhosis.Gastroenterol Jpn. 1989 Dec;24(6):692-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02774169. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1989. PMID: 2606303
-
Significant effects of late evening snack on liver functions in patients with liver cirrhosis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul;34(7):1143-1152. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14665. Epub 2019 May 7. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30883904
Cited by
-
Retracted: Long-Term Carbohydrate-Containing Late-Evening Snack Significantly Improves the Ratio of Branched Chain Amino Acids to Aromatic Amino Acids in Adults with Liver Cirrhosis due to Hepatitis B.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9821414. doi: 10.1155/2024/9821414. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38550013 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Power of Late-Evening Snacks: Practical Ready-to-Prescribe Chart Menu for Patients with Cirrhosis.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 5;15(15):3471. doi: 10.3390/nu15153471. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Organization WH. Guidelines for the prevention, care and treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis B infection . World Health Organization; 2015. https://doi./entity/hiv/pub/hepatitis/hepatitis-b-guidelines/en/index.html . - PubMed
-
- Meng Q. H., Yu H. W., Li J., et al. Inadequate nutritional intake and protein-energy malnutrition involved in acute and chronic viral hepatitis Chinese patients especially in cirrhosis patients. Hepato-Gastroenterology . 2010;57(101):845–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

