Association of KCNQ1rs2237892C⟶T Gene with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34853793
- PMCID: PMC8629679
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6606830
Association of KCNQ1rs2237892C⟶T Gene with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the most common chronic diseases in adults, causing high morbidity and mortality worldwide. In recent years, the prevalence of T2DM has been increasing significantly, and genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have shown that KCNQ1 significantly increases the risk of T2DM.
Objective: To find large-scale evidence on whether the KCNQ1rs2237892C⟶T gene polymorphism is associated with T2DM susceptibility.
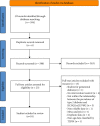
Methods: A comprehensive review of the Chinese and English literature on the association of T2DM with KCNQ1rs2237892 is published by PubMed and Baidu Academic. The included literature was part or all of the studied loci which were evaluated for association with T2DM. Forest plots were made of the included literature to analyze the association of KCNQ1 with polymorphisms of the studied loci, and funnel plots and Egger's test were used to evaluate the publication bias of the selected included literature.
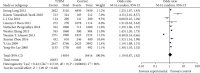
Results: Ten case-control studies including a total of 7027 cases and 8208 controls met our inclusion criteria. Allele (C allele frequency distribution) (OR: 1.19; 95% CI: 0.87,1.62; P < 0.00001), recessive (OR: 0.73; 95% CI: 0.45,1.18; P < 0.00001) genetic model under the full population was observed between KCNQ1rs2237892C⟶T gene polymorphism and T2DM without a significant relationship. In a stratified analysis by race, a meaningful association was found in non-Asian populations under the allelic genetic model, but no association was found in Asian populations.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed no significant association between the rs2237892 polymorphism of the KCNQ1 gene and the risk of T2DM.
Copyright © 2021 Wen-Jia Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that the study was conducted without any commercial or financial relationship.
Figures



Similar articles
-
KCNQ1 rs2237892 C→T gene polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Asian population: a meta-analysis of 15,736 patients.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Feb;18(2):274-82. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12185. Epub 2013 Dec 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24373634 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of KCNQ1 Polymorphisms with the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Meta-Analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jul 3;2020:7145139. doi: 10.1155/2020/7145139. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32695830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variant rs2237892 of KCNQ1 Is Potentially Associated with Hypertension and Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Chinese Han Population.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015 Dec;13(6):364-70. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26678516 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the polymorphisms in KCNQ1 and type 2 diabetes in Chinese Kazakh population.Genet Mol Res. 2016 May 13;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15027503. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27323013
-
Association of CDKAL1 RS10946398 Gene Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: A Meta-Analysis.J Diabetes Res. 2021 Dec 24;2021:1254968. doi: 10.1155/2021/1254968. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 34977253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KCNQ1 rs2237895 gene polymorphism increases susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian populations.World J Diabetes. 2024 Mar 15;15(3):552-564. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i3.552. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38591089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang W., Wang H., Guan X., Niu Q., Li W. Variant rs2237892 of _KCNQ1_ Is Potentially Associated with Hypertension and Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Chinese Han Population. Genomics Proteomics & Bioinformatics . 2015;13(6):364–370. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2015.05.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas . 9th. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2019. https://diabetesatlas.org/en/sections/demographic-and-geographic-outline... . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

