Efficacy and safety of a third-generation oncolytic herpes virus G47Δ in models of human esophageal carcinoma
- PMID: 34853811
- PMCID: PMC8605086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.10.012
Efficacy and safety of a third-generation oncolytic herpes virus G47Δ in models of human esophageal carcinoma
Abstract
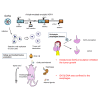
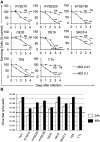
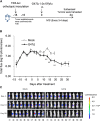
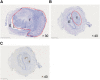
Treatment options are limited for esophageal carcinoma (EC). G47Δ, a triple-mutated, conditionally replicating herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), exhibits enhanced killing of tumor cells with high safety features. Here, we studied the efficacy of G47Δ using preclinical models of human EC. In vitro, G47Δ showed efficient cytopathic effects and replication capabilities in all eight human esophageal cancer cell lines tested. In athymic mice harboring subcutaneous tumors of human EC (KYSE180, TE8, and OE19), two intratumoral injections with G47Δ significantly inhibited the tumor growth. To mimic the clinical treatment situations, we established an orthotopic EC model using luciferase-expressing TE8 cells (TE8-luc). An intratumoral injection with G47Δ markedly inhibited the growth of orthotopic TE8-luc tumors in athymic mice. Furthermore, we evaluated the safety of applying G47Δ to the esophagus in mice. A/J mice inoculated intraesophageally or administered orally with G47Δ (107 plaque-forming units [pfu]) survived for more than 2 months without remarkable symptoms, whereas the majority with wild-type HSV-1 (106 pfu) deteriorated within 10 days. PCR analyses showed that the G47Δ DNA was confined to the esophagus after intraesophageal inoculation and was not detected in major organs after oral administration. Our results provide a rationale for the clinical use of G47Δ for treating EC.
Keywords: G47Δ; biodistribution; esophageal cancer; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; herpes simplex virus; intraesophageal inoculation; oncolytic virus therapy; orthotopic tumor model; preclinical safety; teserpaturev.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.T. owns the patent right for G47Δ in multiple countries, including Japan.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficacy of a Third-Generation Oncolytic Herpes Virus G47Δ in Advanced Stage Models of Human Gastric Cancer.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Apr 8;17:205-215. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.03.022. eCollection 2020 Jun 26. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 32346610 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant use of oncolytic herpes virus G47Δ prevents local recurrence after insufficient resection in tongue cancer models.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023 Jul 19;30:72-85. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.07.002. eCollection 2023 Sep 21. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023. PMID: 37583387 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of orthotopic malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors with oncolytic herpes simplex virus.Neuro Oncol. 2014 Aug;16(8):1057-66. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not317. Epub 2014 Jan 26. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24470552 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic virus therapy using genetically engineered herpes simplex viruses.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2060-4. doi: 10.2741/2823. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981691 Review.
-
Teserpaturev/G47Δ: First Approval.BioDrugs. 2022 Sep;36(5):667-672. doi: 10.1007/s40259-022-00553-7. BioDrugs. 2022. PMID: 36098872 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Status and Challenges of Oncolytic Virotherapy for the Treatment of Glioblastoma.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 26;16(6):793. doi: 10.3390/ph16060793. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dilemma of HSV-1 Oncolytic Virus Delivery: The Method Choice and Hurdles.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 12;24(4):3681. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043681. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of HPV-Related Uterine Cervical Cancer with a Third-Generation Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus in Combination with an Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 19;24(3):1988. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031988. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768352 Free PMC article.
-
HSV: The scout and assault for digestive system tumors.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 28;10:1142498. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1142498. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36926680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fusion peptide is superior to co-expressing subunits for arming oncolytic herpes virus with interleukin 12.Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Mar 25;3(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00270-4. Commun Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 36966232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Lagergren J., Smyth E., Cunningham D., Lagergren P. Oesophageal cancer. Lancet. 2017;390:2383–2396. - PubMed
-
- Wang V.E., Grandis J.R., Ko A.H. New strategies in esophageal carcinoma: translational insights from signaling pathways and immune checkpoints. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22:4283–4290. - PubMed
-
- Ajani J.A., D'Amico T.A., Almhanna K., Bentrem D.J., Besh S., Chao J., Das P., Denlinger C., Fanta P., Fuchs C.S., et al. Esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancers, version 1.2015. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2015;13:194–227. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

