Practical approach to linear EUS examination of the mediastinum
- PMID: 34854401
- PMCID: PMC8785678
- DOI: 10.4103/EUS-D-21-00019
Practical approach to linear EUS examination of the mediastinum
Abstract
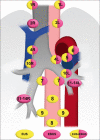
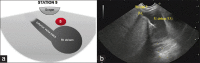
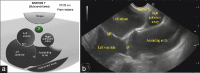
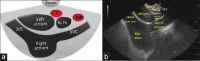
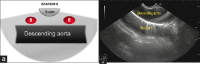
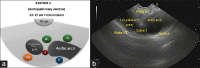
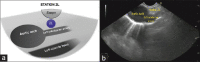
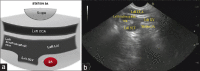
EUS has become a substantial diagnostic and therapeutic modality for many anatomical regions. The extent of endosonographic assessment is wide, and among others, allows for the evaluation of the mediastinal anatomy and related pathologies such as mediastinal lymphadenopathy and staging of central malignant lung lesions. Moreover, EUS assessment has proved more accurate in detecting small lesions missed by standard imaging examinations such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance. Endosonographically, various mediastinal anatomical landmarks and stations can be visualized by transesophageal scanning, thus providing arranged systematic examination of the mediastinum. In addition, the correct position during the examination is crucial for EUS-guided procedures such as tissue sampling and drainage of mediastinal abscesses. The evolution of EUS-guided diagnostic and interventional procedures has contributed to the increasing importance of understanding the mediastinal anatomy during the EUS examination.
Keywords: EUS; anatomy; linear; mediastinal stations.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linear endoscopic ultrasound: Current uses and future perspectives in mediastinal examination.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 7;30(33):3803-3809. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i33.3803. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39351425 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning-based system for mediastinum station localization in linear EUS (with video).Endosc Ultrasound. 2023 Sep-Oct;12(5):417-423. doi: 10.1097/eus.0000000000000011. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Endosc Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 37969169 Free PMC article.
-
Practical approach to linear EUS examination of the liver.Endosc Ultrasound. 2021 May-Jun;10(3):161-167. doi: 10.4103/EUS-D-20-00162. Endosc Ultrasound. 2021. PMID: 33904508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined endobronchial and esophageal endosonography for the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline, in cooperation with the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons (ESTS).Endoscopy. 2015 Jun;47(6):545-59. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1392040. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Endoscopy. 2015. PMID: 26030890
-
Choose the best route: ultrasound-guided transbronchial and transesophageal needle aspiration with echobronchoscope in the diagnosis of mediastinal and pulmonary lesions.Minerva Med. 2015 Oct;106(5 Suppl 1):13-9. Minerva Med. 2015. PMID: 27427262 Review.
Cited by
-
Linear endoscopic ultrasound: Current uses and future perspectives in mediastinal examination.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 7;30(33):3803-3809. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i33.3803. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39351425 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of wet-heparinized suction on the quality of mediastinal solid tumor specimens obtained by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: a retrospective study from a single center.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Jun 14;23(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02845-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37316772 Free PMC article.
-
Mediastinal Nodal Staging Performance of Combined Endobronchial and Esophageal Endosonography in Lung Cancer Cases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Surg. 2022 May 23;9:890993. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.890993. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35677749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic modalities in the mediastinum and the role of bronchoscopy in mediastinal assessment: a narrative review.Mediastinum. 2024 Dec 6;8:51. doi: 10.21037/med-24-32. eCollection 2024. Mediastinum. 2024. PMID: 39781205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A deep learning-based system for mediastinum station localization in linear EUS (with video).Endosc Ultrasound. 2023 Sep-Oct;12(5):417-423. doi: 10.1097/eus.0000000000000011. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Endosc Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 37969169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jenssen C, Annema JT, Clementsen P, et al. Ultrasound techniques in the evaluation of the mediastinum, part 2: Mediastinal lymph node anatomy and diagnostic reach of ultrasound techniques, clinical work up of neoplastic and inflammatory mediastinal lymphadenopathy using ultrasound techniques and how to learn mediastinal endosonography. J Thorac Dis. 2015;7:E439–58. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tanoue LT. Staging of non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;29:248–60. - PubMed
-
- Rivera MP, Mehta AC, Wahidi MM. Establishing the diagnosis of lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e142S–65S. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert C, Akulian J, Ortiz R, et al. Novel bronchoscopic strategies for the diagnosis of peripheral lung lesions: Present techniques and future directions. Respirology. 2014;19:636–44. - PubMed

