Hydrogen-rich bath with nano-sized bubbles improves antioxidant capacity based on oxygen radical absorbing and inflammation levels in human serum
- PMID: 34854419
- PMCID: PMC8690854
- DOI: 10.4103/2045-9912.330692
Hydrogen-rich bath with nano-sized bubbles improves antioxidant capacity based on oxygen radical absorbing and inflammation levels in human serum
Abstract
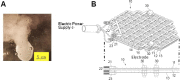
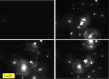
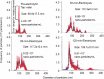
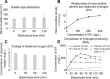
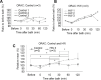
This study compared the effects of hydrogen-water (HW) bath on the oxygen radical absorption-based antioxidant capacity and the inflammatory indicator, C-reactive protein (CRP), in serum between healthy volunteers and inflammatory/collagen disease-patients. The HW bath apparatus supplied nano-bubbles with a diameter of 110 ± 10 nm and 338-682 μg/L of dissolved hydrogen after 120 minutes electrolysis, and nano-bubbles increased to 9.91 × 107/mL along with the increase of correlative dissolved hydrogen. Ten-minute HW bath increased the oxygen radical absorption-based antioxidant capacity to 110.9 ± 9.2% at post-bathing 120 minutes, although unaltered with 10-minute normal water bath at 40°C in healthy subjects. The CRP level was repressed to 70.2 ± 12.1% at 120 minutes after HW bath, although rather increased for normal water bath. In the patients with connective tissue diseases, the CRP level was repressed to 3-24% upon 9 days to 4 months of HW bathing. In another six patients with diverse autoimmune-related diseases, upon daily HW bathing as long as 2-25 months, the pre-bathing CRP level of 5.31 mg/dL decreased to 0.24 mg/dL being within the standard-range, with relief of visible inflammatory symptoms for some cases. Thus, the HW bath with high-density nano-bubbles has beneficial effects on serum antioxidant capacity, inflammation, and the skin appearance. The study was approved by the Committee of Ethics, Japanese Center of Anti-Aging Medical Sciences (Authorization No. H-15-03-2, on January 15, 2019), which was a non-profitable organization officially authenticated by the Hiroshima Prefecture Government of Japan.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; anti-inflammatory effect; antioxidant capacity; electrolysis; human serum; human skin; hydrogen-rich water; nano-bubble.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures






Similar articles
-
Effects of hydrogen-rich water bath on visceral fat and skin blotch, with boiling-resistant hydrogen bubbles.Med Gas Res. 2019 Apr-Jun;9(2):68-73. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.260647. Med Gas Res. 2019. PMID: 31249254 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Nano-Bubble Water Suppresses ROS Generation, Adipogenesis, and Interleukin-6 Secretion in Hydrogen-Peroxide- or PMA-Stimulated Adipocytes and Three-Dimensional Subcutaneous Adipose Equivalents.Cells. 2021 Mar 11;10(3):626. doi: 10.3390/cells10030626. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33799840 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hydrogen-rich water prepared by alternating-current-electrolysis on antioxidant activity, DNA oxidative injuries, and diabetes-related markers.Med Gas Res. 2020 Jul-Sep;10(3):114-121. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.296041. Med Gas Res. 2020. PMID: 33004708 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of in vitro tests for antioxidant and immunomodulatory capacities of compounds.Phytomedicine. 2014 Jan 15;21(2):164-71. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Sep 14. Phytomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24041614 Review.
-
Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;144(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.04.006. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24769081 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular hydrogen as a potential mediator of the antitumor effect of inulin consumption.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 3;15(1):11482. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96346-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40181080 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the Application of Molecular Hydrogen in Medical Skin Cosmetology.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025 Mar 3;18:511-523. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S500255. eCollection 2025. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40061044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micro-Nano Bubbles: A New Field of Eco-Friendly Cleaning.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Mar 23;15(7):480. doi: 10.3390/nano15070480. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40214526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobubbles: a bridge connecting nanomedicine and gas medicine.Med Gas Res. 2025 Jun 1;15(2):214-215. doi: 10.4103/mgr.MEDGASRES-D-24-00115. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Med Gas Res. 2025. PMID: 40070196 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Topically Applied Molecular Hydrogen Normalizes Skin Parameters Associated with Oxidative Stress: A Pilot Study.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 14;14(6):729. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060729. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colavitti R, Finkel T. Reactive oxygen species as mediators of cellular senescence. IUBMB Life. 2005;57:277–281. - PubMed
-
- Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2007;297:842–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

