Vaginal Complications after Cystectomy: Results from a Medicare Sample
- PMID: 34854750
- PMCID: PMC8916976
- DOI: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002336
Vaginal Complications after Cystectomy: Results from a Medicare Sample
Abstract
Purpose: Cystectomy with a vaginal-sparing approach may be associated with unique complications specific to the female population. The objective of this study was to estimate the incidence of vaginal complications (defined to include vaginal prolapse, vaginal fistula, dyspareunia and vaginal cuff dehiscence/evisceration) after cystectomy and to determine risk factors for these complications.
Materials and methods: Women 65 years or older undergoing cystectomy for any indication were identified by procedural codes in the Medicare Limited Data Set 5% sample from January 1, 2011 to December 31, 2017. Patients experiencing a vaginal complication after cystectomy were compared to those who did not. Demographic and biological factors that could increase likelihood of complications were identified and time to development of complications determined. Cumulative incidence was calculated using cumulative incidence function. Multivariable cause-specific Cox proportional hazards model assessed risk factors for vaginal complications.
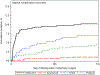
Results: In all, 481 women undergoing cystectomy were identified during the study period, and 37.2% were younger than 70 years old. The majority (378, 79%) had bladder cancer, and 401 (83.4%) underwent an incontinent conduit or catheterizable channel diversion. Within 2 years of cystectomy, 93 patients (19.5%) had 1 or more complications on record. Vaginal cuff dehiscence had the highest cumulative incidence, occurring in 49 patients (10.2%). Over the entire study period (2011-2017), 102 women (21.2%) were diagnosed with a vaginal complication, and 27 (5.6%) received an intervention.
Conclusions: Among women who undergo cystectomy, vaginal complications occur at rates higher than expected with over 20% of women experiencing a complication and over a quarter of those diagnosed undergoing intervention.
Keywords: cystectomy; dyspareunia; fistula; prolapse.
Figures
Comment in
-
Editorial Comment.J Urol. 2022 Apr;207(4):796. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002336.02. Epub 2021 Dec 22. J Urol. 2022. PMID: 34933566 No abstract available.
-
Editorial Comment.J Urol. 2022 Apr;207(4):795-796. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002336.01. Epub 2021 Dec 22. J Urol. 2022. PMID: 34933567 No abstract available.
References
-
- Grossman HB, Natale RB, Tangen CM, et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy plus Cystectomy Compared with Cystectomy Alone for Locally Advanced Bladder Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;349:859–866. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg S, Miranda G, Ginsberg DA. Neobladder-Vaginal fistula: The University of Southern California experience. Neurourol Urodyn 2018;37;1380. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical