Mass spectrometric detection of KRAS protein mutations using molecular imprinting
- PMID: 34854867
- PMCID: PMC8675027
- DOI: 10.1039/d1nr03180e
Mass spectrometric detection of KRAS protein mutations using molecular imprinting
Abstract
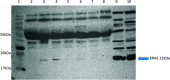
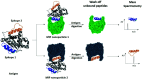
Cancer is a disease of cellular evolution where single base changes in the genetic code can have significant impact on the translation of proteins and their activity. Thus, in cancer research there is significant interest in methods that can determine mutations and identify the significant binding sites (epitopes) of antibodies to proteins in order to develop novel therapies. Nano molecularly imprinted polymers (nanoMIPs) provide an alternative to antibodies as reagents capable of specifically capturing target molecules depending on their structure. In this study, we used nanoMIPs to capture KRAS, a critical oncogene, to identify mutations which when present are indicative of oncological progress. Herein, coupling nanoMIPs (capture) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (detection), LC-MS has allowed us to investigate mutational assignment and epitope discovery. Specifically, we have shown epitope discovery by generating nanoMIPs to a recombinant KRAS protein and identifying three regions of the protein which have been previously assigned as epitopes using much more time-consuming protocols. The mutation status of the released tryptic peptide was identified by LC-MS following capture of the conserved region of KRAS using nanoMIPS, which were tryptically digested, thus releasing the sequence of a non-conserved (mutated) region. This approach was tested in cell lines where we showed the effective genotyping of a KRAS cell line and in the plasma of cancer patients, thus demonstrating its ability to diagnose precisely the mutational status of a patient. This work provides a clear line-of-sight for the use of nanoMIPs to its translation from research into diagnostic and clinical utility.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Modulation of EGFR Activity by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles Targeting Intracellular Epitopes.Nano Lett. 2023 Nov 8;23(21):9677-9682. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c01374. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Nano Lett. 2023. PMID: 37902816 Free PMC article.
-
Does the protein corona take over the selectivity of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles? The biological challenges to recognition.J Proteomics. 2020 May 15;219:103736. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103736. Epub 2020 Mar 19. J Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32198073
-
Epitope approach in molecular imprinting of antibodies.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019 Aug 15;1124:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.05.024. Epub 2019 May 25. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31176265
-
Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications.Adv Mater. 2020 Jan;32(3):e1806328. doi: 10.1002/adma.201806328. Epub 2019 May 15. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 31090976 Review.
-
Personalized medicine in non-small-cell lung cancer: is KRAS a useful marker in selecting patients for epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy?J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 1;28(31):4769-77. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.4365. Epub 2010 Oct 4. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20921461 Review.
Cited by
-
Nano-molecularly imprinted polymers (nanoMIPs) as a novel approach to targeted drug delivery in nanomedicine.RSC Adv. 2022 Feb 1;12(7):3957-3968. doi: 10.1039/d1ra08385f. eCollection 2022 Jan 28. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35425427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep plasma and tissue proteome profiling of knockout mice reveals pathways associated with Svep1 deficiency.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Jan 10;11:100283. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100283. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 39895831 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of EGFR Activity by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles Targeting Intracellular Epitopes.Nano Lett. 2023 Nov 8;23(21):9677-9682. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c01374. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Nano Lett. 2023. PMID: 37902816 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Organ Lysate Imprinting: For Precision Recognition and Analysis of Organ-Derived Proteins.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2025 Dec 15;39(23):e10125. doi: 10.1002/rcm.10125. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2025. PMID: 40873137 Free PMC article.
-
KRAS mutations detection methodology: from RFLP to CRISPR/Cas based methods.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Oct 5;24(5):183. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01421-z. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39367162 Review.
References
-
- Andre F. Arnedos M. Baras A. S. Baselga J. Bedard P. L. Berger M. F. Bierkens M. Calvo F. Cerami E. Chakravarty D. et al. . Cancer Discovery. 2017;7:818–831. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0151. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

