Subcellular localization of D2 receptors in the murine substantia nigra
- PMID: 34854963
- PMCID: PMC8930450
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-021-02432-3
Subcellular localization of D2 receptors in the murine substantia nigra
Abstract
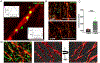
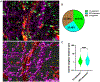
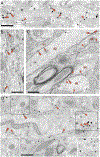
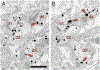
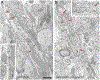
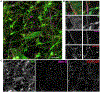
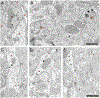
G-protein-coupled D2 autoreceptors expressed on dopamine neurons (D2Rs) inhibit transmitter release and cell firing at axonal endings and somatodendritic compartments. Mechanistic details of somatodendritic dopamine release remain unresolved, partly due to insufficient information on the subcellular distribution of D2Rs. Previous studies localizing D2Rs have been hindered by a dearth of antibodies validated for specificity in D2R knockout animals and have been limited by the small sampling areas imaged by electron microscopy. This study utilized sub-diffraction fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy to examine D2 receptors in a superecliptic pHlourin GFP (SEP) epitope-tagged D2 receptor knockin mouse. Incubating live slices with an anti-SEP antibody achieved the selective labeling of plasma membrane-associated receptors for immunofluorescent imaging over a large area of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc). SEP-D2Rs appeared as puncta-like structures along the surface of dendrites and soma of dopamine neurons visualized by antibodies to tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). TH-associated SEP-D2Rs displayed a cell surface density of 0.66 puncta/µm2, which corresponds to an average frequency of 1 punctum every 1.50 µm. Separate ultrastructural experiments using silver-enhanced immunogold revealed that membrane-bound particles represented 28% of total D2Rs in putative dopamine cells within the SNc. Structures immediately adjacent to dendritic membrane gold particles were unmyelinated axons or axon varicosities (40%), astrocytes (19%), other dendrites (7%), or profiles unidentified (34%) in single sections. Some apposed profiles also expressed D2Rs. Fluorescent and ultrastructural analyses also provided the first visualization of membrane D2Rs at the axon initial segment, a compartment critical for action potential generation. The punctate appearance of anti-SEP staining indicates there is a population of D2Rs organized in discrete signaling sites along the plasma membrane, and for the first time, a quantitative estimate of spatial frequency is provided.
Keywords: Autoreceptor; D2 receptor; Dopamine; Substantia nigra; Ultrastructure.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
None of the authors report a conflict of interest. One author (SRS) acknowledges being a Co-Editor-In-Chief of this journal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cav1.3 channels control D2-autoreceptor responses via NCS-1 in substantia nigra dopamine neurons.Brain. 2014 Aug;137(Pt 8):2287-302. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu131. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Brain. 2014. PMID: 24934288 Free PMC article.
-
Desensitized D2 autoreceptors are resistant to trafficking.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 29;7(1):4379. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04728-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28663556 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D2 receptors regulate the action potential threshold by modulating T-type calcium channels in stellate cells of the medial entorhinal cortex.J Physiol. 2019 Jul;597(13):3363-3387. doi: 10.1113/JP277976. Epub 2019 May 28. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31049961
-
The role of D2-autoreceptors in regulating dopamine neuron activity and transmission.Neuroscience. 2014 Dec 12;282:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.01.025. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24463000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electron microscopic immunolabeling of transporters and receptors identifies transmitter-specific functional sites envisioned in Cajal's neuron.Prog Brain Res. 2002;136:145-55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(02)36014-x. Prog Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12143378 Review.
Cited by
-
Preservation of dendritic D2 receptor transmission in substantia nigra dopamine neurons with age.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 19;13(1):1025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28174-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36658269 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic-like axo-axonal transmission from striatal cholinergic interneurons onto dopaminergic fibers.Neuron. 2022 Sep 21;110(18):2949-2960.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.07.011. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35931070 Free PMC article.
-
Immunolocalization of kappa opioid receptors in the axon initial segment of a group of embryonic mesencephalic dopamine neurons.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 May 11;12:411-418. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.05.002. eCollection 2022 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35746971 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D2 receptors in hilar mossy cells regulate excitatory transmission and hippocampal function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 12;120(50):e2307509120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2307509120. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38064513 Free PMC article.
-
A mathematical model for the role of dopamine-D2 self-regulation in the production of ultradian rhythms.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 May 3;20(5):e1012082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012082. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38701077 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

