Combined acquisition of diffusion and T2*-weighted measurements using simultaneous multi-contrast magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 34855052
- PMCID: PMC9188537
- DOI: 10.1007/s10334-021-00976-3
Combined acquisition of diffusion and T2*-weighted measurements using simultaneous multi-contrast magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Object: In this work, we present a technique called simultaneous multi-contrast imaging (SMC) to acquire multiple contrasts within a single measurement. Simultaneous multi-slice imaging (SMS) shortens scan time by allowing the repetition time (TR) to be reduced for a given number of slices. SMC imaging preserves TR, while combining different scan types into a single acquisition. This technique offers new opportunities in clinical protocols where examination time is a critical factor and multiple image contrasts must be acquired.
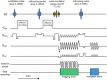
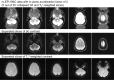
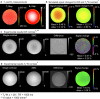
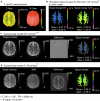
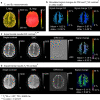
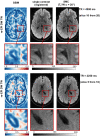
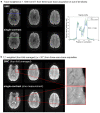
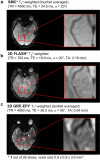
Materials and methods: High-resolution, navigator-corrected, diffusion-weighted imaging was performed simultaneously with T2*-weighted acquisition at 3 T in a phantom and in five healthy subjects using an adapted readout-segmented EPI sequence (rs-EPI).
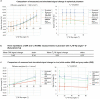
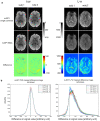
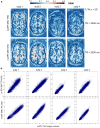
Results: The results demonstrated that simultaneous acquisition of two contrasts (here diffusion-weighted imaging and T2*-weighting) with SMC imaging is feasible with robust separation of contrasts and minimal effect on image quality.
Discussion: The simultaneous acquisition of multiple contrasts reduces the overall examination time and there is an inherent registration between contrasts. By using the results of this study to control saturation effects in SMC, the method enables rapid acquisition of distortion-matched and well-registered diffusion-weighted and T2*-weighted imaging, which could support rapid diagnosis and treatment of acute stroke.
Keywords: Diffusion; Echo-planar imaging; Stroke.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

