Association of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 34855819
- PMCID: PMC8638857
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260479
Association of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: A meta-analysis
Abstract
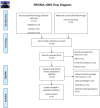
It has been suggested that small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) could cause nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), but this association was not examined in children by meta-analysis. This meta-analysis aimed to determine the association between SIBO and NAFLD in children. The electronic databases PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched for studies published before April 22, 2021. The outcome was the association between SIBO and NAFLD. Three studies and 205 children were included. All three studies reported the association between SIBO and NAFLD. Children with SIBO were more likely to have NAFLD (odds ratio = 5.27, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.66-16.68, P<0.001; I2 = 63.5%, Pheterogeneity = 0.065). When directly pooling the reported relative risks (RR) from two studies, children with NAFLD had an over 2-fold increased relative risk of developing SIBO (RR = 2.17, 05%CI: 1.66-2.82, P<0.001; I2 = 0.0%, Pheterogeneity = 0.837). This meta-analysis reports a possible association between SIBO and NAFLD in children.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(7):1592–609. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.001 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Collaboration NCDRF. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390(10113):2627–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5735219. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson EL, Howe LD, Jones HE, Higgins JP, Lawlor DA, Fraser A. The Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PloS one. 2015;10(10):e0140908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140908 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4626023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous