Potential role of the ABCG2-Q141K polymorphism in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 34855903
- PMCID: PMC8638943
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260957
Potential role of the ABCG2-Q141K polymorphism in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
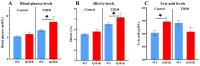
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex metabolic disease and variations in multispecific membrane transporter functions may affect T2DM development, complications or treatment. In this work we have analyzed the potential effects of a major polymorphism, the Q141K variant of the ABCG2 transporter in T2DM. The ABCG2 protein is a multispecific xeno- and endobiotic transporter, affecting drug metabolism and playing a key role in uric acid extrusion. The ABCG2-Q141K variant, with reduced expression level and function, is present in 15-35% of individuals, depending on the genetic background of the population, and has been shown to significantly affect gout development. Several other diseases, including hypertension, chronic renal failure, and T2DM have also been reported to be associated with high serum uric acid levels, suggesting that ABCG2 may also play a role in these conditions. In this work we have compared relatively small cohorts (n = 203) of T2DM patients (n = 99) and healthy (n = 104) individuals regarding the major laboratory indicators of T2DM and determined the presence of the SNP rs2231142 (C421A), resulting the ABCG2-Q141K protein variant. We found significantly higher blood glucose and HbA1c levels in the T2DM patients carrying the ABCG2-Q141K variant. These findings may emphasize the potential metabolic role of ABCG2 in T2DM and indicate that further research should explore how prevention and treatment of this disease may be affected by the frequent polymorphism of ABCG2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. J.Cs. was an employee of Cellpharma Kft., a medical biotechnology and pharmaceutical research and development company. This affiliation does not alter our adherence to all PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)-mediated glyburide transport: effect of the C421A/Q141K BCRP single-nucleotide polymorphism.Drug Metab Dispos. 2010 May;38(5):740-4. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.030791. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010. PMID: 20159988
-
The C421A (Q141K) polymorphism enhances the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR)-dependent regulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Mar 15;104:139-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.02.011. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26903388
-
Contrasting roles of the ABCG2 Q141K variant in prostate cancer.Exp Cell Res. 2017 May 1;354(1):40-47. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.03.020. Epub 2017 Mar 11. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28300564 Free PMC article.
-
ABCG2 as a therapeutic target candidate for gout.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Feb;22(2):123-129. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1420167. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 29264928 Review.
-
The frequency of rs2231142 in ABCG2 among Asian subgroups: implications for personalized rosuvastatin dosing.Pharmacogenomics. 2023 Jan;24(1):15-26. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2022-0155. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Pharmacogenomics. 2023. PMID: 36651271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of the ABCG2 rs2231142 variant with the Framingham Cardiovascular Disease Risk score in the Taiwanese population.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 11;10(18):e37839. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37839. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39315221 Free PMC article.
-
rs2231142 (421 C>A, Q141K) Is More Functionally Influential than rs2231137 (34 G>A, V12M) on Anticancer Drug Resistance Mediated by the ABCG2 Haplotype In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 1;26(15):7428. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157428. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806557 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabis Pharmacogenomics: A Path to Personalized Medicine.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Apr 17;45(4):3479-3514. doi: 10.3390/cimb45040228. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37185752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Variants of the Human Thiamine Transporter (SLC19A3, THTR2)-Potential Relevance in Metabolic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 25;26(7):2972. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072972. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243602 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Modulation of the GLUT1 Transporter Expression-Potential Relevance in Complex Diseases.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;11(11):1669. doi: 10.3390/biology11111669. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421383 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

