Turbulence-induced formation of emulsion gels
- PMID: 34856449
- PMCID: PMC8640544
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105847
Turbulence-induced formation of emulsion gels
Abstract
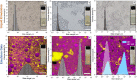
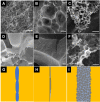
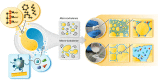
Emulsion gels have a wide range of applications. We report on a facile and versatile method to produce stable emulsion gels with tunable rheological properties. Gel formation is triggered by subjecting a mixture containing aqueous colloidal particle (CP) suspensions and water-immiscible liquids to intense turbulence, generated by low frequency (20 kHz) ultrasound or high-pressure homogenization. Through systematic investigations, requisite gel formation criteria are established with respect to both formulation and processing, including ratio/type of liquid pairs, CP properties, and turbulence conditions. Based on the emulsion microstructure and rheological properties, inter-droplet bridging and CP void-filling are proposed as universal stabilization mechanisms. These mechanisms are further linked to droplet-size scaling and sphere close-packing theory, distinctive from existing gel-conferring models. The study thereby provides the foundation for advancing the production of emulsion gels that can be tailored to a wide range of current and emerging applications in the formulation and processing of food, cosmetics or pharmaceutical gels, and in material science.
Keywords: Colloidal Particles; Emulsion Gels; Turbulent Flow; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Dickinson E. Emulsion gels: the structuring of soft solids with protein-stabilized oil droplets. Food Hydrocolloids. 2012;28(1):224–241.
-
- Lupi F.R., Gabriele D., Seta L., Baldino N., de Cindio B., Marino R. Rheological investigation of pectin-based emulsion gels for pharmaceutical and cosmetic uses. Rheol. Acta. 2015;54(1):41–52.
-
- Hu Z., Patten T., Pelton R., Cranston E.D. Synergistic stabilization of emulsions and emulsion gels with water-soluble polymers and cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2015;3(5):1023–1031.
-
- Gallegos C., Franco J.M. Rheology of food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999;4(4):288–293.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

