Feasibility and preliminary efficacy of acupuncture for angina in an underserved diverse population
- PMID: 34856826
- PMCID: PMC8881402
- DOI: 10.1177/09645284211055754
Feasibility and preliminary efficacy of acupuncture for angina in an underserved diverse population
Abstract
Purpose: Stable angina is ischemic chest pain on exertion or with emotional stress. Despite guideline-directed therapy, up to 30% of patients have suboptimal pain relief. The aims of this study were to: (1) determine the feasibility and acceptability of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) of acupuncture; and (2) evaluate preliminary efficacy of acupuncture with respect to reduction of pain and increased functional status and health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
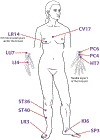
Methods: Participants with stable angina for ⩾1 month received either a standardized acupuncture protocol, twice per week for 5 weeks, or an attention control protocol. Measures included the McGill Pain Questionnaire (average pain intensity (API), pain now) and the Seattle Angina Questionnaire-7 (functional status, symptoms, and HRQoL). Feasibility was defined as ⩾80% recruitment, ⩾75% retention following enrollment, and ⩾80% completion. Descriptive statistics and mixed-effects linear regression were used for analysis.
Results: The sample (n = 24) had a mean age of 59 ± 12 years, was predominantly female (63%), and represented minority groups (8% White, 52% Black, 33% Hispanic, and 8% Other). Feasibility was supported by 79% retention and 89% completion rates. The recruitment rate (68%) was slightly lower than expected. Acceptability scores were 87.9% for the acupuncture group and 51.7% for the control group. Outcomes were significantly better for the acupuncture versus control groups (API, b = -2.1 (1.1), p = 0.047; functional status, b = 27.6 (7.2), p < 0.001; and HRQoL, b = 38.8 (11.9), p = 0.001).
Conclusions and implications: Acupuncture was feasible and acceptable in our diverse sample. We were slightly under the recruitment target of 80%, but participants who started the study had a high likelihood of completing it. Acupuncture shows promise for stable angina, but its effectiveness needs to be confirmed by a larger, adequately powered RCT.
Trial registration number: NCT02914834 (ClinicalTrials.gov).
Keywords: acupuncture; integrative therapy; ischemic heart disease; stable angina.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sensitized-points acupuncture versus routine integrative acupuncture for chronic low back pain: A randomized-controlled feasibility study.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2025 Jan;38(1):101-112. doi: 10.1177/10538127241289343. Epub 2025 Jan 9. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 39970453 Clinical Trial.
-
Acupuncture to Improve Symptoms for Stable Angina: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2019 Jul 29;8(7):e14705. doi: 10.2196/14705. JMIR Res Protoc. 2019. PMID: 31359872 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for chronic pain in adults with sickle cell disease: a mixed-methods pilot study.Acupunct Med. 2021 Dec;39(6):612-618. doi: 10.1177/09645284211017303. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Acupunct Med. 2021. PMID: 34080441 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Manual Acupuncture Plus Usual Care Versus Usual Care Alone in the Treatment of Endometriosis-Related Chronic Pelvic Pain: A Randomized Controlled Feasibility Study.J Altern Complement Med. 2021 Oct;27(10):841-849. doi: 10.1089/acm.2021.0004. Epub 2021 Jun 23. J Altern Complement Med. 2021. PMID: 34161143 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of acupuncture on aromatase inhibitor-induced arthralgia in patients with breast cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Breast. 2017 Jun;33:132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Breast. 2017. PMID: 28384564 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of acupoint selection and prescription rules of acupuncture for treatment of stable angina pectoris based on a Traditional Chinese Medicine inheritance calculation platform: A systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e31466. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031466. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626434 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates acute myocardial ischemic injury in mice by regulating the β1 adrenergic receptor and post-receptor protein kinase A signaling pathway.Acupunct Med. 2024 Dec;42(6):342-355. doi: 10.1177/09645284241298716. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Acupunct Med. 2024. PMID: 39579035 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture Dosage and Its Correlation with Effectiveness in Patients with Chronic Stable Angina: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial.J Pain Res. 2025 Jan 10;18:105-125. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S489880. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 39811250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Acupuncture on Human Metabolomic Profiles: A Systematic Review.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 11;14(10):542. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100542. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016; 133(4): e38–e360. - PubMed
-
- Camm AJ, Manolis A, Ambrosio G, et al. Unresolved issues in the management of chronic stable angina. Int J Cardiol 2015; 201: 200–207. - PubMed
-
- Longmore RB, Spertus JA, Alexander KP, et al. Angina frequency after myocardial infarction and quality of life in older versus younger adults: the Prospective Registry Evaluating Myocardial Infarction: event and recovery study. Am Heart J 2011; 161(3): 631–638. - PubMed