Functional enrichment of alternative splicing events with NEASE reveals insights into tissue identity and diseases
- PMID: 34857024
- PMCID: PMC8638120
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02538-1
Functional enrichment of alternative splicing events with NEASE reveals insights into tissue identity and diseases
Abstract
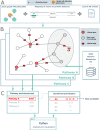
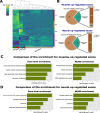
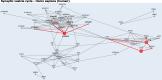
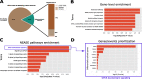
Alternative splicing (AS) is an important aspect of gene regulation. Nevertheless, its role in molecular processes and pathobiology is far from understood. A roadblock is that tools for the functional analysis of AS-set events are lacking. To mitigate this, we developed NEASE, a tool integrating pathways with structural annotations of protein-protein interactions to functionally characterize AS events. We show in four application cases how NEASE can identify pathways contributing to tissue identity and cell type development, and how it highlights splicing-related biomarkers. With a unique view on AS, NEASE generates unique and meaningful biological insights complementary to classical pathways analysis.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; Differential splicing; Dilated cardiomyopathy; Disease pathways; Functional enrichment; Multiple sclerosis; Platelet activation; Protein-protein interactions; Systems biology.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting protein interaction network perturbation by alternative splicing with semi-supervised learning.Cell Rep. 2021 Nov 23;37(8):110045. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110045. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34818539
-
Robust and annotation-free analysis of alternative splicing across diverse cell types in mice.Elife. 2022 Mar 1;11:e73520. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73520. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35229721 Free PMC article.
-
RNA binding protein 24 deletion disrupts global alternative splicing and causes dilated cardiomyopathy.Protein Cell. 2019 Jun;10(6):405-416. doi: 10.1007/s13238-018-0578-8. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Protein Cell. 2019. PMID: 30267374 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of alternative splicing variants in multiple sclerosis - A systematic review.Autoimmun Rev. 2019 Jul;18(7):721-732. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.05.010. Epub 2019 May 4. Autoimmun Rev. 2019. PMID: 31059848
-
Functional roles of alternative splicing factors in human disease.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015 May-Jun;6(3):311-26. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1276. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015. PMID: 25630614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative splicing impacts microRNA regulation within coding regions.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023 Sep 11;5(3):lqad081. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad081. eCollection 2023 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37705830 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of alternative splicing in time course data using Spycone.Bioinformatics. 2023 Jan 1;39(1):btac846. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac846. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36579860 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of the effects of splicing on the diversity of post-translational modifications in protein isoforms using PTM-POSE.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 27:2024.01.10.575062. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.10.575062. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cell Syst. 2025 Jul 16;16(7):101318. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2025.101318. PMID: 38260432 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
EXPANSION: a webserver to explore the functional consequences of protein-coding alternative splice variants in cancer genomics.Bioinform Adv. 2023 Sep 26;3(1):vbad135. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbad135. eCollection 2023. Bioinform Adv. 2023. PMID: 37810457 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of the effects of splicing on the diversity of post-translational modifications in protein isoforms using PTM-POSE.Cell Syst. 2025 Jul 16;16(7):101318. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2025.101318. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Cell Syst. 2025. PMID: 40513562
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

