Inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 ameliorates ischemia/hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier injury through the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway
- PMID: 34857032
- PMCID: PMC8641178
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-021-00356-x
Inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 ameliorates ischemia/hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier injury through the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway
Abstract
Background: Disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) after a stroke can lead to brain injury and neurological impairment. Previous work confirmed the involvement of the immunoproteasome subunit of low molecular mass peptide 2 (LMP2) in the pathophysiology of ischemia stroke. However, the relationship between the immunoproteasome LMP2 and the BBB remains unclear.
Methods: Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R). Three days before MCAO, the rats were treated with lentivirus-mediated LMP2 shRNA preparations by stereotactical injection into the ipsilateral hemispheric region. The rat brain microvascular endothelial cell (RBMVEC) line was exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) to mimic ischemic conditions in vitro. The RNA interference-mediated knockdown of LMP2 or β-catenin was analysed in vivo and in vitro. Analysis of the quantity of extravasated Evans blue (EB) and cerebral fluorescent angiography were performed to evaluate the integrity of the BBB. Immunofluorescence and Western blotting were employed to detect the expression of target proteins. Cell migration was evaluated using a scratch migration assay. The results of immunofluorescence, Western blotting and cell migration were quantified using the software ImageJ (Version 1.53m). Parametric data from different groups were compared using one-way ANOVA followed by the least significant difference (LSD) test.
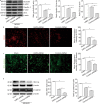
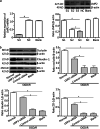
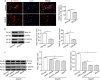
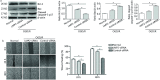
Results: Cerebral ischemia led to lower levels of structural components of the BBB such as tight junction proteins (occludin, claudin-1 and ZO-1) in the MCAO/R group compared with the sham group (P < 0.001). However, inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 restored the expression of these proteins, resulting in higher levels of occludin, claudin-1 and ZO-1 in the LMP2-shRNA group compared with the control-shRNA group (P < 0.001). In addition, inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 contributed to higher microvascular density and decreased BBB permeability [e.g., the quantity of extravasated EB: LMP2-shRNA group (58.54 ± 7.37) µg/g vs. control-shRNA group (103.74 ± 4.32) µg/g, P < 0.001], and promoted the upregulation of Wnt-3a and β-catenin proteins in rats following MCAO/R. In vitro experiments, OGD/R induced marked upregulation of LMP2, proapoptotic protein Bax and cleaved caspase-3, and downregulation of occludin, claudin-1, ZO-1 and Bcl-2, as well as inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway Wnt-3a and β-catenin proteins in RBMVECs, compared with the control group under normal culture conditions (P < 0.001). However, silencing of LMP2 gene expression reversed these protein changes and promoted proliferation and migration of RBMVECs following OGD/R. Silencing of β-catenin by transfection of RBMVECs with β-catenin-siRNA aggravated the downregulation of tight junction proteins, and reduced the proliferation and migration of RBMVECs following OGD/R, compared with the control-siRNA group (P < 0.001). LMP2-siRNA and β-catenin-siRNA co-transfection partly counteracted the beneficial effects of silencing LMP2-siRNA on the levels of tight junction proteins in RBMVECs exposed to OGD/R.
Conclusion: This study suggests that inhibition of the immunoproteasome LMP2 ameliorates ischemia/hypoxia-induced BBB injury, and that the molecular mechanism involves the immunoproteasome-regulated activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway under ischemic conditions.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Cerebral ischemia; Immunoproteasome; Oxygen–glucose deprivation/reperfusion; Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
JLX001 attenuates blood-brain barrier dysfunction in MCAO/R rats via activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Nov 1;260:118221. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118221. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32768578
-
Lithium alleviates blood-brain barrier breakdown after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion by upregulating endothelial Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Mar 15;186:108474. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108474. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33524408
-
PFT-α protects the blood-brain barrier through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway after acute ischemic stroke.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Sep 30;23(4):314. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01237-3. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37777676
-
Developmental regulation of barrier- and non-barrier blood vessels in the CNS.J Intern Med. 2022 Jul;292(1):31-46. doi: 10.1111/joim.13263. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 33665890 Review.
-
Regulation of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability via JNK Signaling Pathway: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Ischemic Stroke, Alzheimer's Disease and Brain Tumors.Molecules. 2025 May 28;30(11):2353. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112353. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40509244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Baicalein Inhibits Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through SIRT6-Mediated FOXA2 Deacetylation to Promote SLC7A11 Expression.eNeuro. 2024 Oct 4;11(10):ENEURO.0174-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0174-24.2024. Print 2024 Oct. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 39299807 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Potential of Immunotherapies in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Treatment: Mechanistic Dissection of Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses.Aging Dis. 2023 Oct 1;14(5):1533-1554. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0126. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37196120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted role of nitric oxide in vascular dementia.Med Gas Res. 2025 Dec 1;15(4):496-506. doi: 10.4103/mgr.MEDGASRES-D-24-00158. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Med Gas Res. 2025. PMID: 40300885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of PHGDH with IGF2BP1 facilitates m6A-dependent stabilization of TCF7L2 mRNA to confer multidrug resistance in gastric cancer.Oncogene. 2025 Jul;44(25):2064-2077. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03374-4. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40188301
-
Damage mechanism and therapy progress of the blood-brain barrier after ischemic stroke.Cell Biosci. 2023 Nov 1;13(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01126-z. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37915036 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

